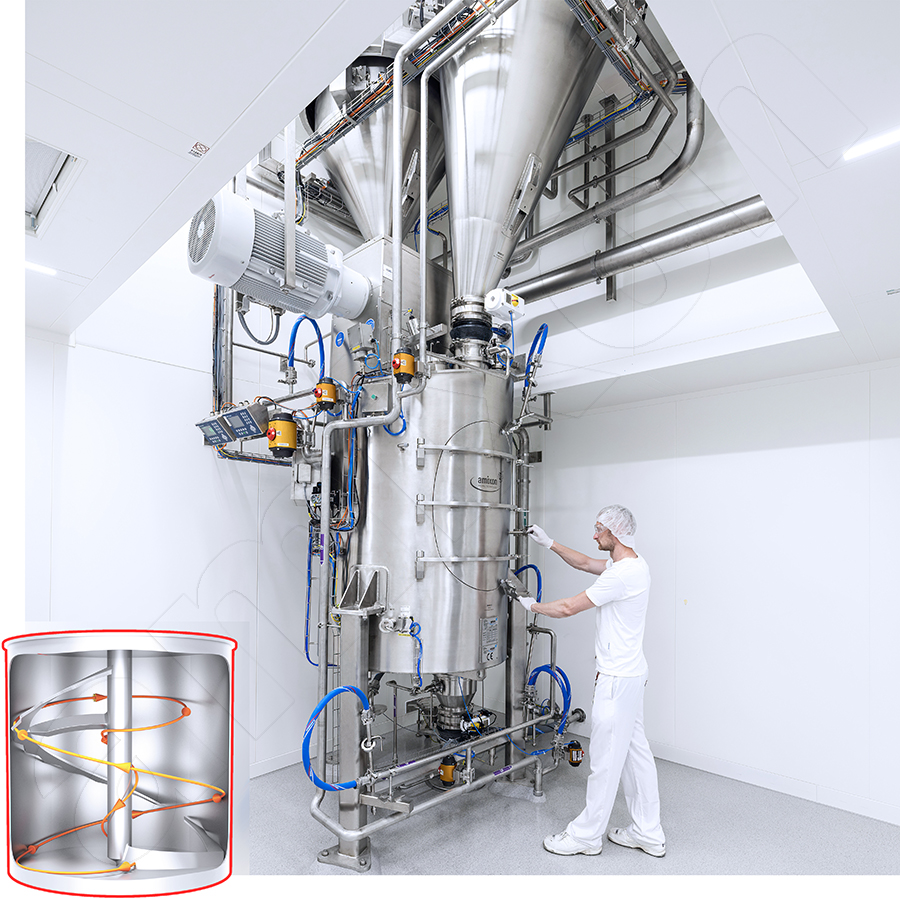
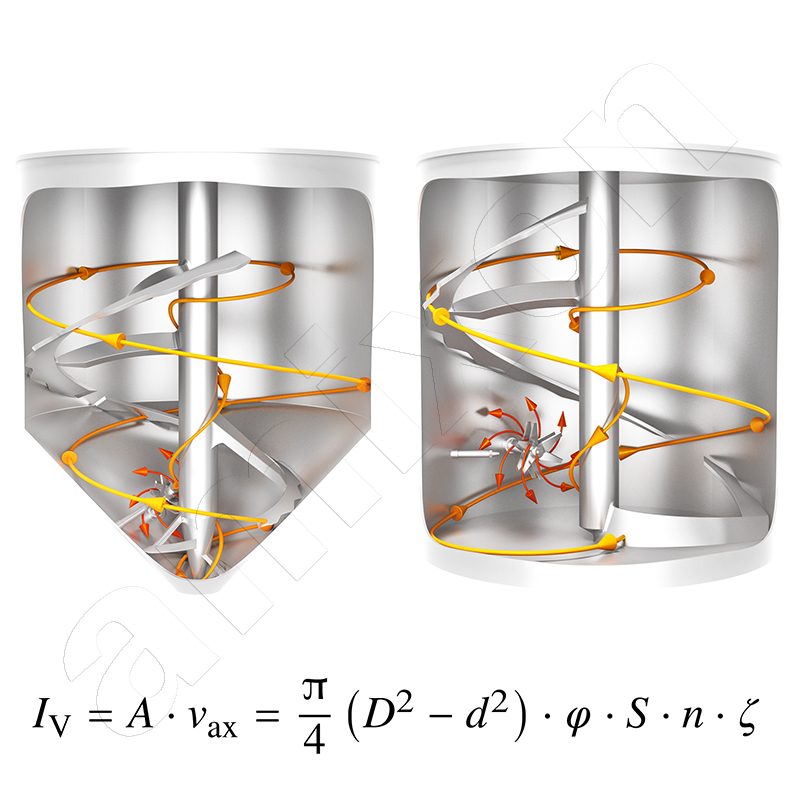
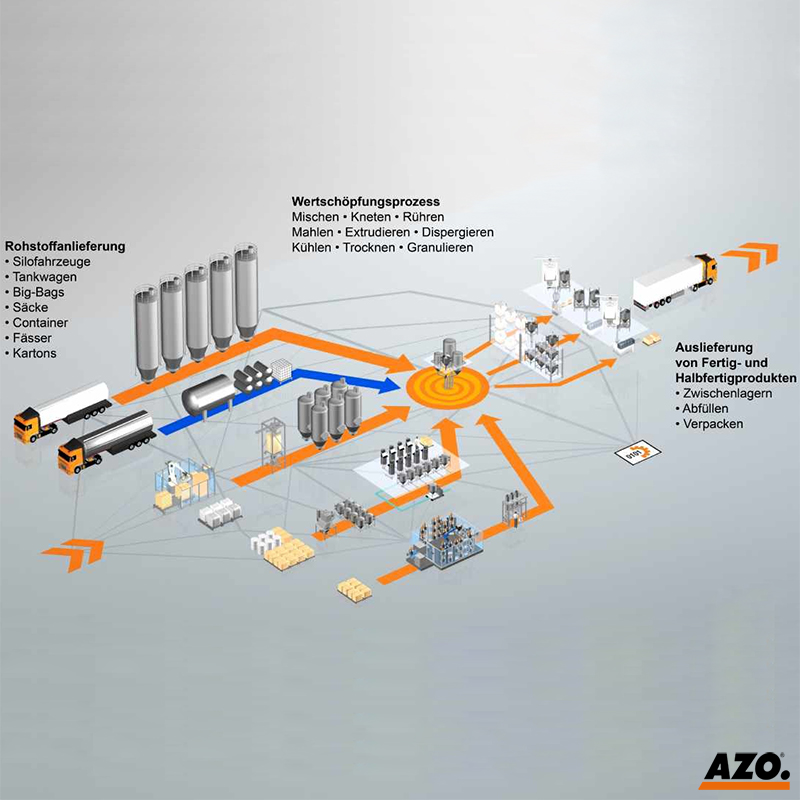
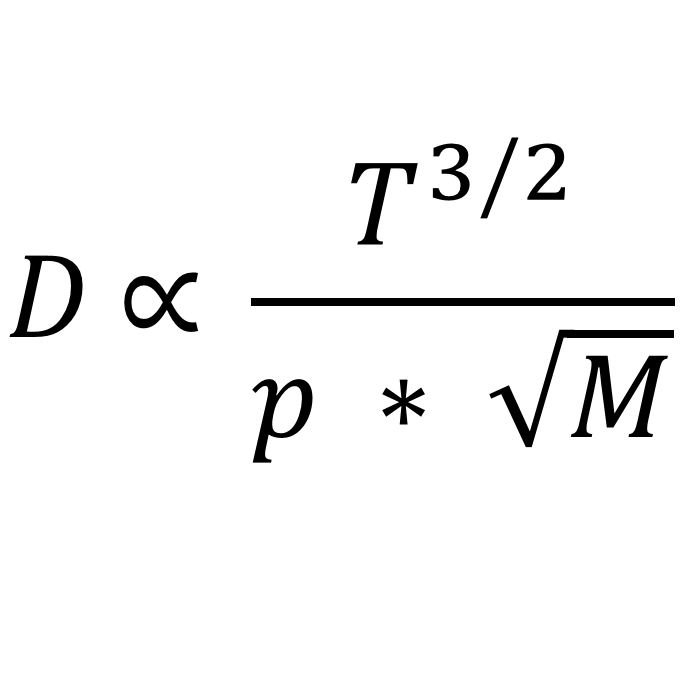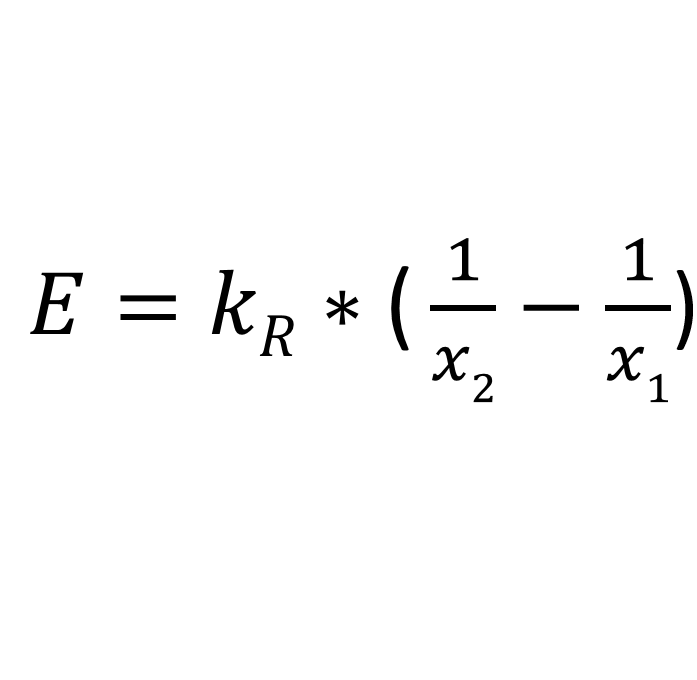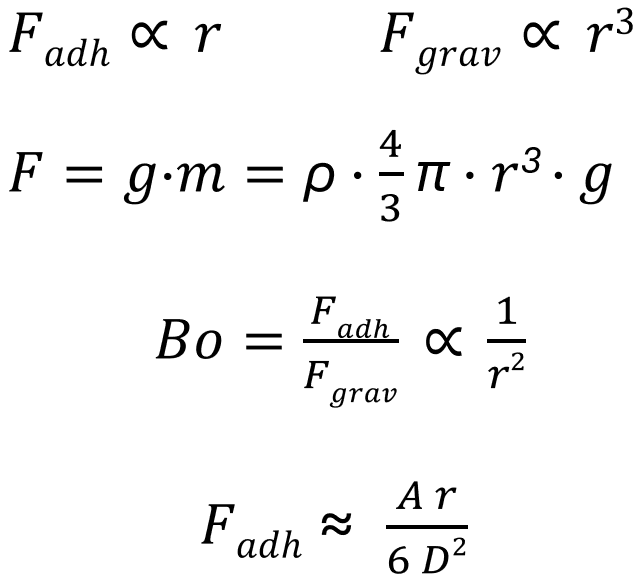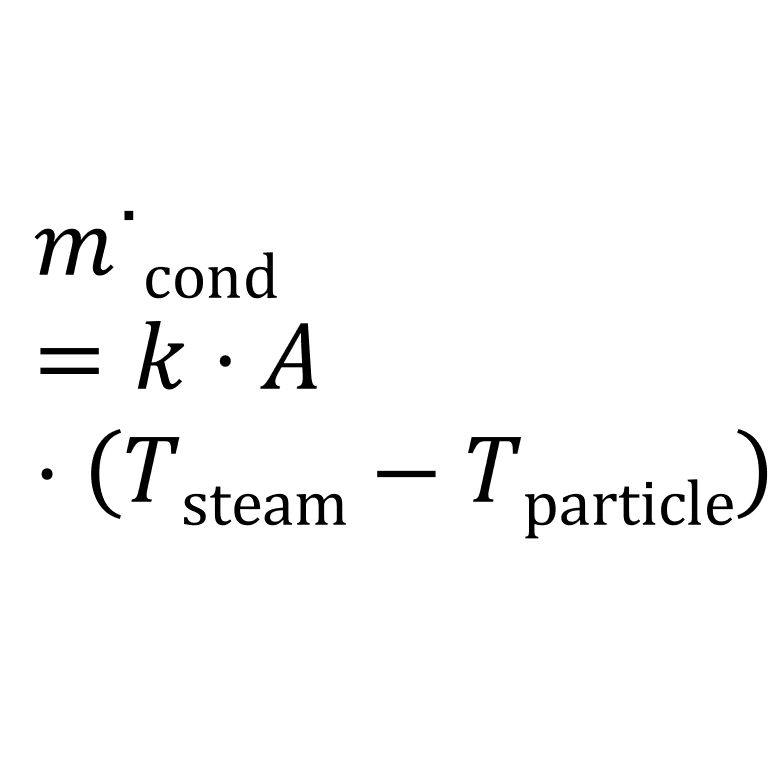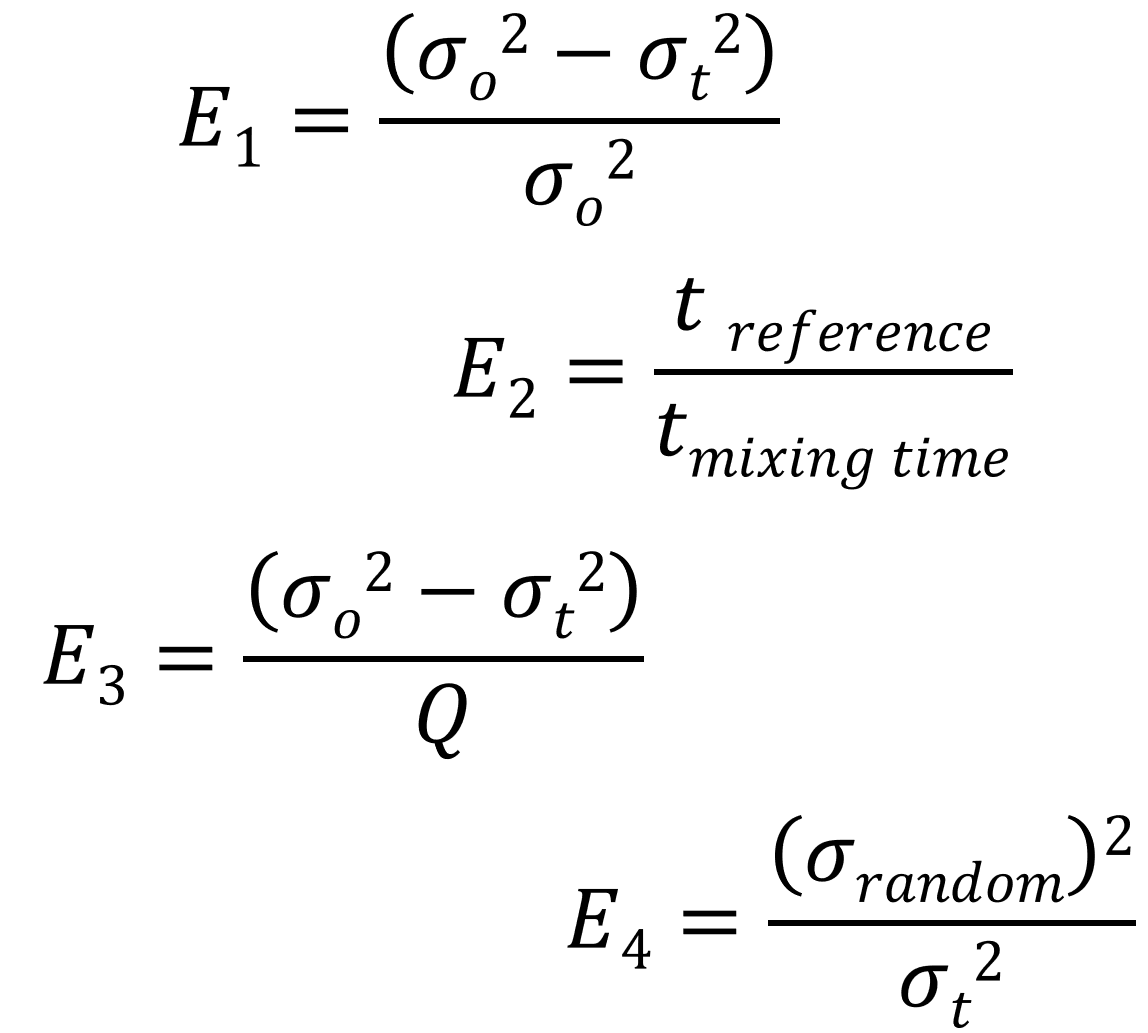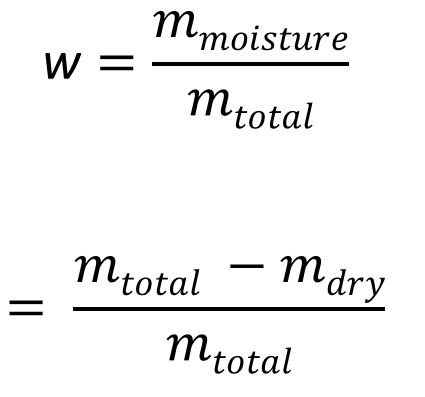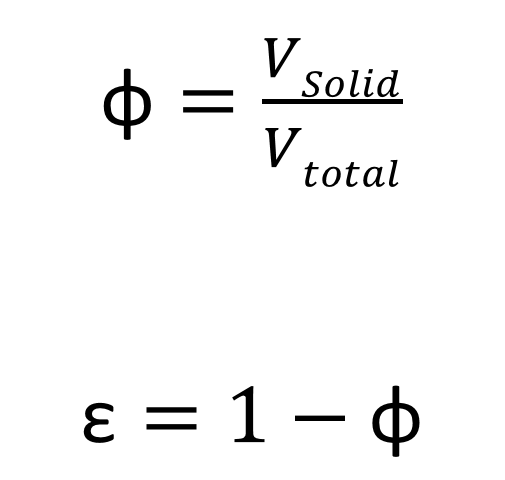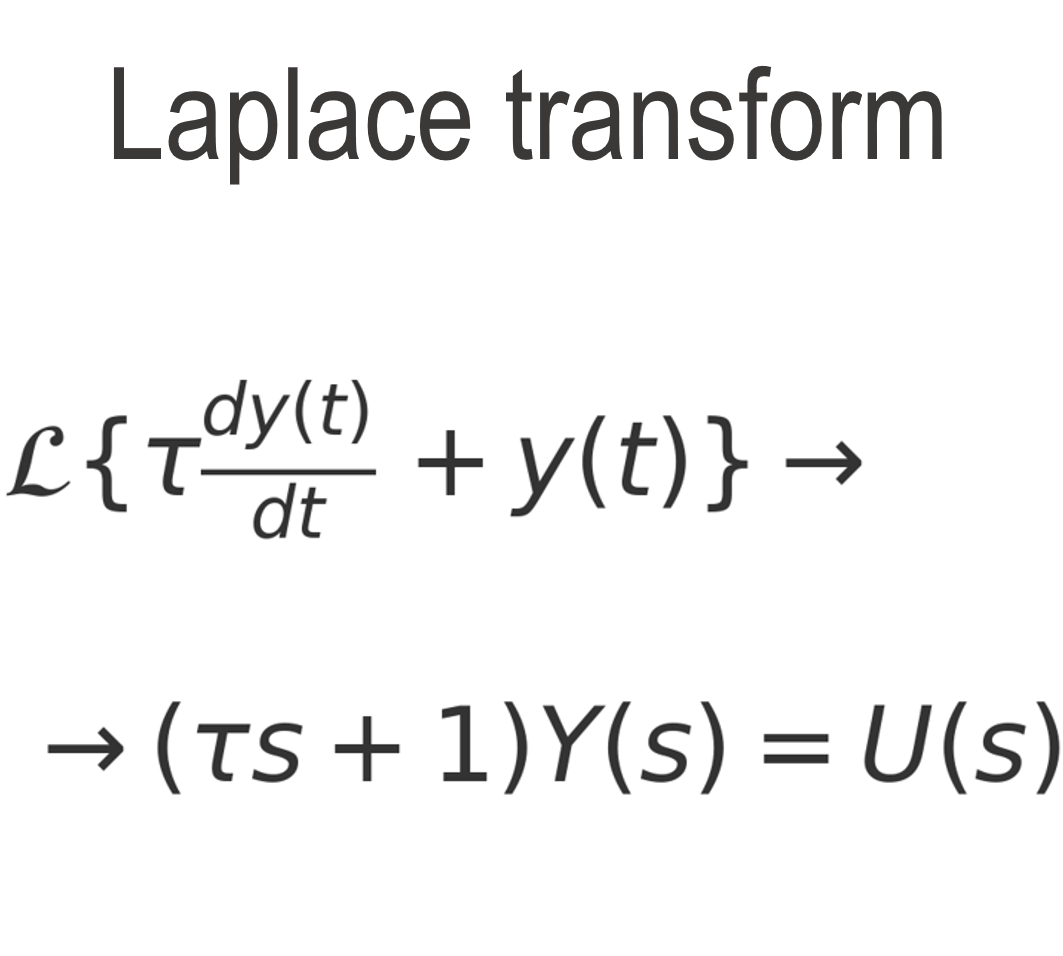Abrasion
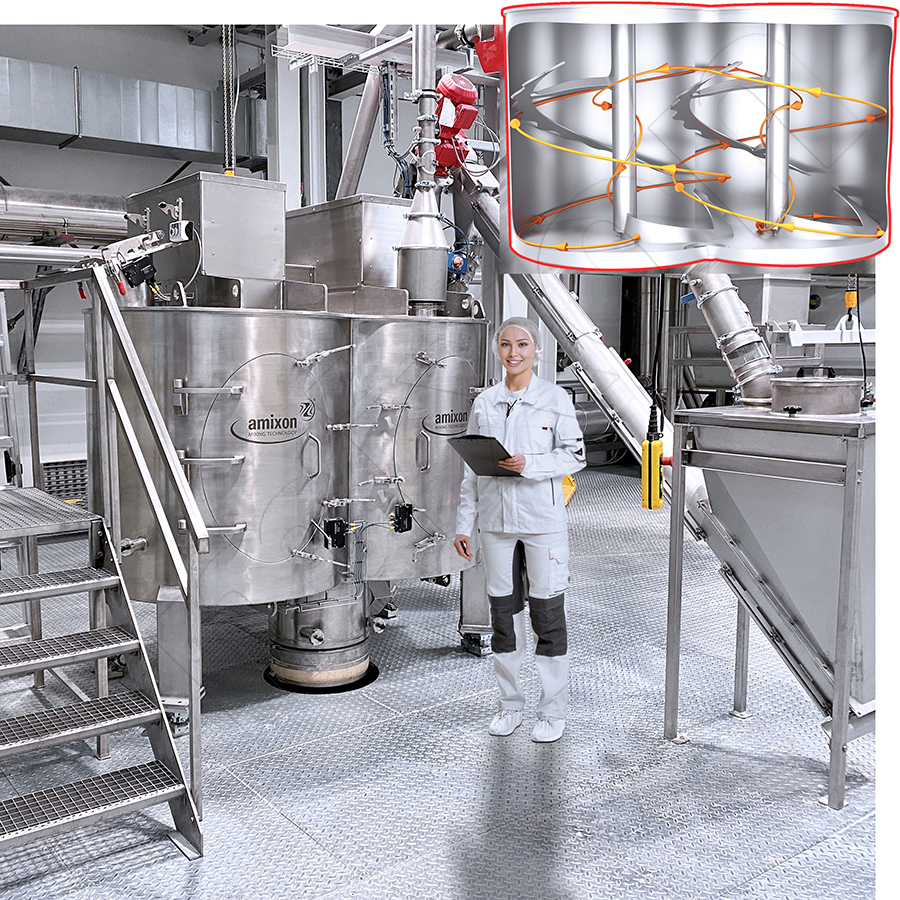
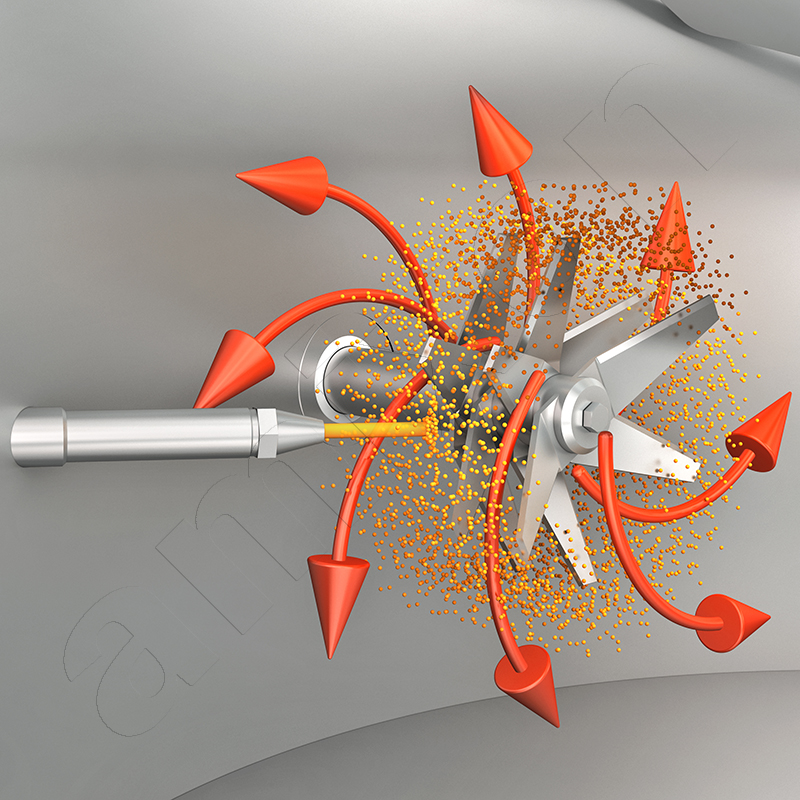
Attrition, wear are important terms when bulk solids are mixed or conveyed. Abrasion always occurs in the contact area when two bodies move relative to each other. In this process, the harder of the two bodies damages the surface of the softer solid. This form of abrasion is referred to as abrasion.
Read moreAbsolute pressure
In the construction of apparatus for thermal and mechanical process engineering, system pressures play an important role. For example, process engineering apparatus has a maximum permissible overpressure due to its design.
Read moreAbsorption tendency
The term absorption must be considered in connection with the term adsorption. Both processes describe the accumulation of a foreign substance on an adsorbent or absorbent. However, the difference is as follows:
Read moreAdhesion
In the bulk materials industry, the terms adhesion and cohesion describe the behaviour of particles.
Adhesion refers to the forces of attraction between different materials. In the case of powders, adhesion influences how strongly the particles adhere to the surface of a mixer. High adhesion forces can lead to deposits in mixers. These deposits are sources of contamination and affect the purity of the mixed batch.
Read moreAgglomeration
In powder processing, agglomeration is defined as a process of accumulating fine material into cohesive units such as pellets or granules. In simple terms, powder agglomeration shifts fine, powdery particles to a coarser size range that facilitates handling and storage.
Read moreair retention capacity
Fluidised powders with a pronounced air retention capacity are rather undesirable. They are difficult to process.
Read moreAllergens and allergen management
Allergens are substances that can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Pollen from plants in the air can also be allergens. In the food and pharmaceutical industries, allergens include proteins and enzymes. In the chemical industry, allergens include certain plasticisers and metal compounds.
Read moreArnature; shut-off valve
A shut-off valve is a technical component that opens or closes the flow of solids, liquids or gases in pipelines. It is crucial that the mechanical operation takes place outside of the medium to be controlled. This is what distinguishes it from a flap or door.
Read moreAseptic
The word "aseptic" is derived from the term "sepsis". The organism of mammals and humans develops counter-reactions when blood poisoning is present. A severe counter-reaction is called sepsis. It can even destroy the body's own tissue and organs. The "a" at the beginning of the word symbolizes the opposite.
Read moreatmospheric oxygen
Image on the left: Pressure relief device from Rembe. Oxygen is highly reactive and promotes oxidative chemical reactions.
Read moreAutomatic wet cleaning
The challenges are:
- Safe cleaning.
- Safe drying.
- Minimal manpower.
- Automated documentation.
- Fastest possible release for production.
Ball mixer
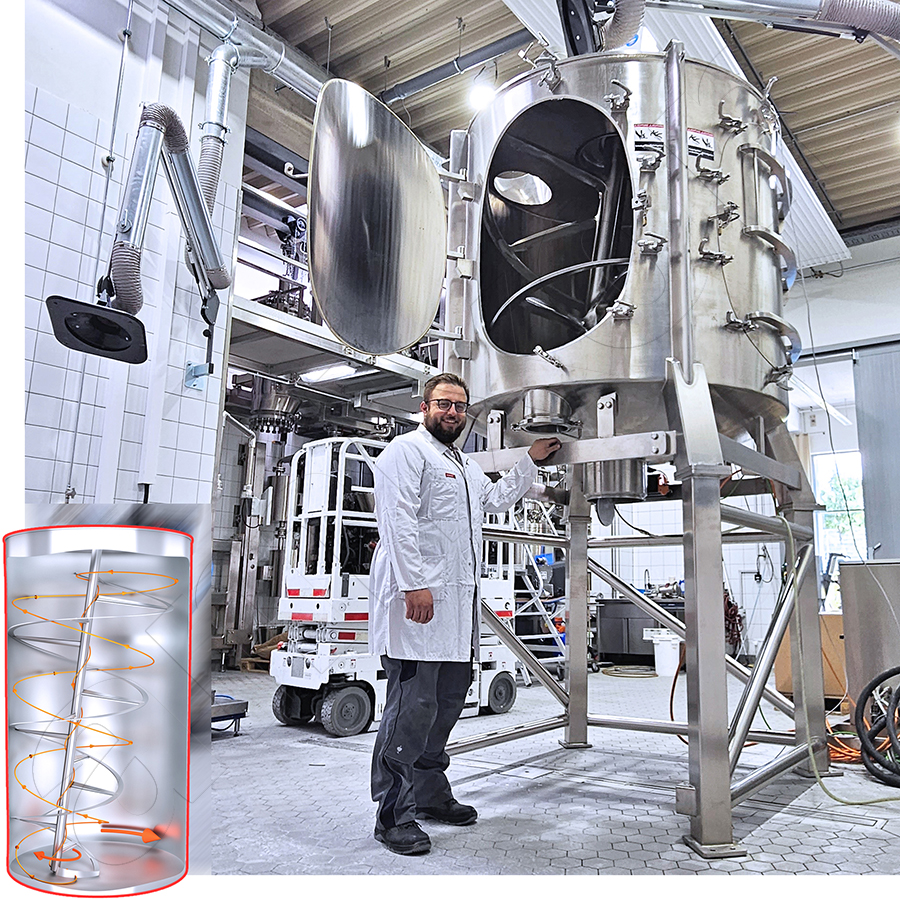
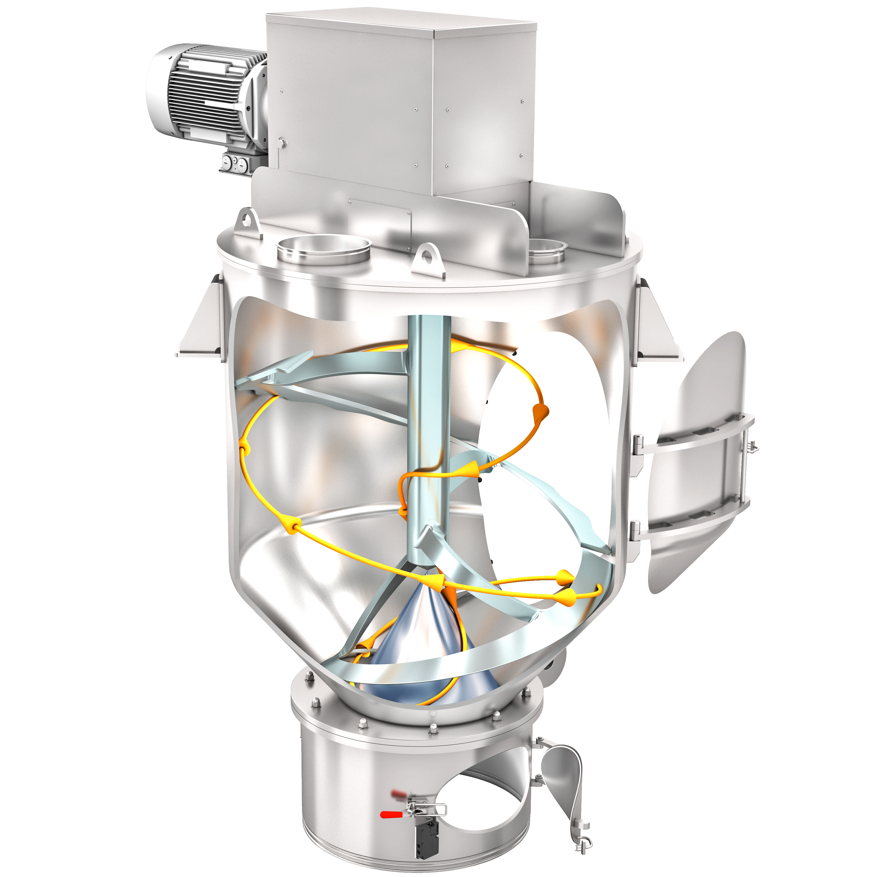
Powdery bulk materials can be mixed in a spherical container. The sphere is usually installed in a fixed position. At least one mixing tool rotates in the sphere.
Read moreBall segment valve
The difference between a ball valve and a ball segment valve is that in a ball segment valve, only the ball cap serves as the closing element.
Read moreBatch Batch size
The term batch is often used in bulk goods processing. Most high-quality bulk materials/powder mixtures are processed in batches. - In contrast to continuous processing.
Read moreBatch size
Although ‘batch’ is an English word, it is often used without translation in bulk materials technology.
Read moreBins
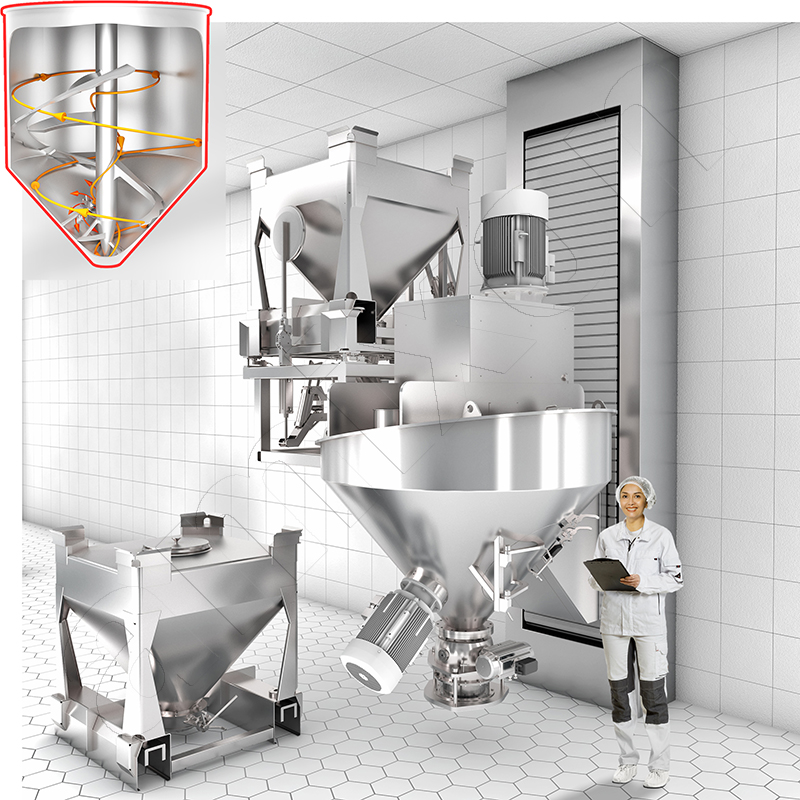
A bin is a logistical unit for holding, storing and transporting raw materials, semi-finished or finished goods. The aim is to transport products safely, efficiently and in a manner that is easy to handle. Containers are ubiquitous in industry, both for solid and liquid substances. Opposite, you can see an IBC bulk container from amixon®, which also serves as a mixing vessel.
Read moreBlending silo
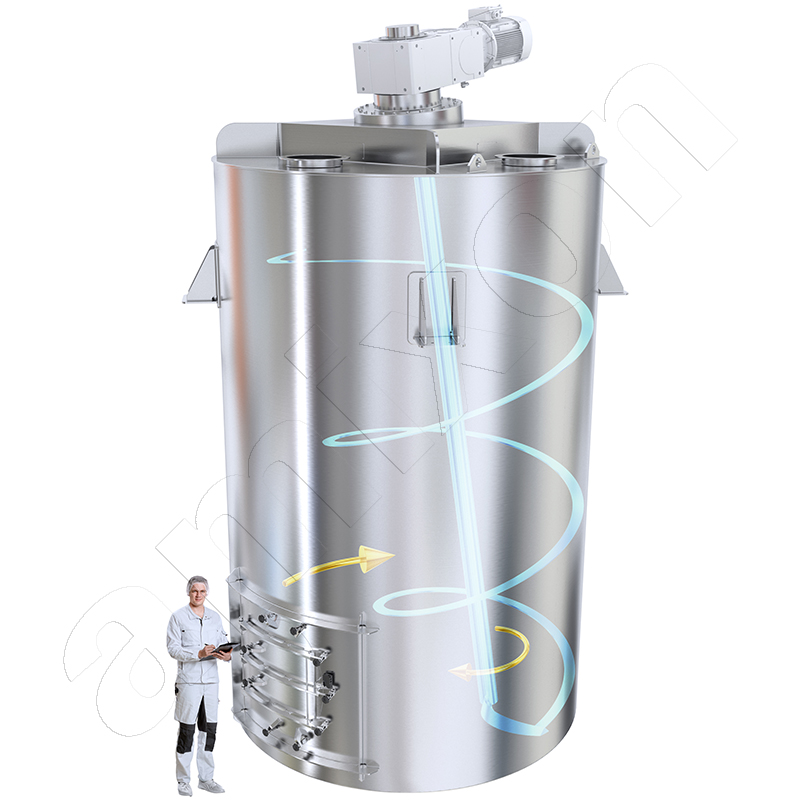
amixon® manufactures the Gyraton® mixer. The Gyraton® can store up to 100 m³ of bulk material and mix it with high precision. It combines the function of a silo with that of a precision mixer. This is achieved regardless of the material properties: dry, moist, free-flowing, poorly flowing, different bulk densities, different grain sizes, etc.
Read moreBoiler flow mixer
As a rule, there should always be a high filling level in the boiler flow mixer.
Read moreBulk density Bulk density measurement
There are numerous methods for measuring bulk density. A particularly simple method is described here.
Read moreCalcination
Calcination takes place at relatively high temperatures. However, these are below the melting temperature.
Read moreCeramic coatings
Ceramic coatings are characterised by high hardness, wear resistance and chemical inertness.
Read moreChamber filter press
A chamber filter press is a discontinuously operating mechanical system for solid-liquid separation.
Read moreCIP cleaning-in-place
CIP (Cleaning In Place) is a process for the automated cleaning of process equipment. The definition and objective of CIP can be described as follows: Creating clean internal surfaces of a production unit without significantly changing the internal elements required for production. Depending on the water pressure during cleaning, a distinction is made between low-pressure cleaning (up to 3 bar), medium-pressure cleaning (up to 10 bar) and high-pressure cleaning (25-65 bar). The process is sometimes also referred to as "washing in place" (WIP).
Read moreCoating
The coating process for powder processing is based on the principle of particle agglomeration as a side operation of the powder mixing or fluid bed process. Interparticle adhesion effects of small particles can be particularly large. They result from Van der Vals forces and electromagnetic forces. If the particles are only a few nanometers in size, they can coat active ingredient particles particularly well. Coating attempts to enlarge the mixture particles in a shell-like manner. In short, coating processes optimize properties of a bulk material in terms of shelf life, optical appearance, solubility, dust binding, flow behavior, durability, chemical reaction and much more.
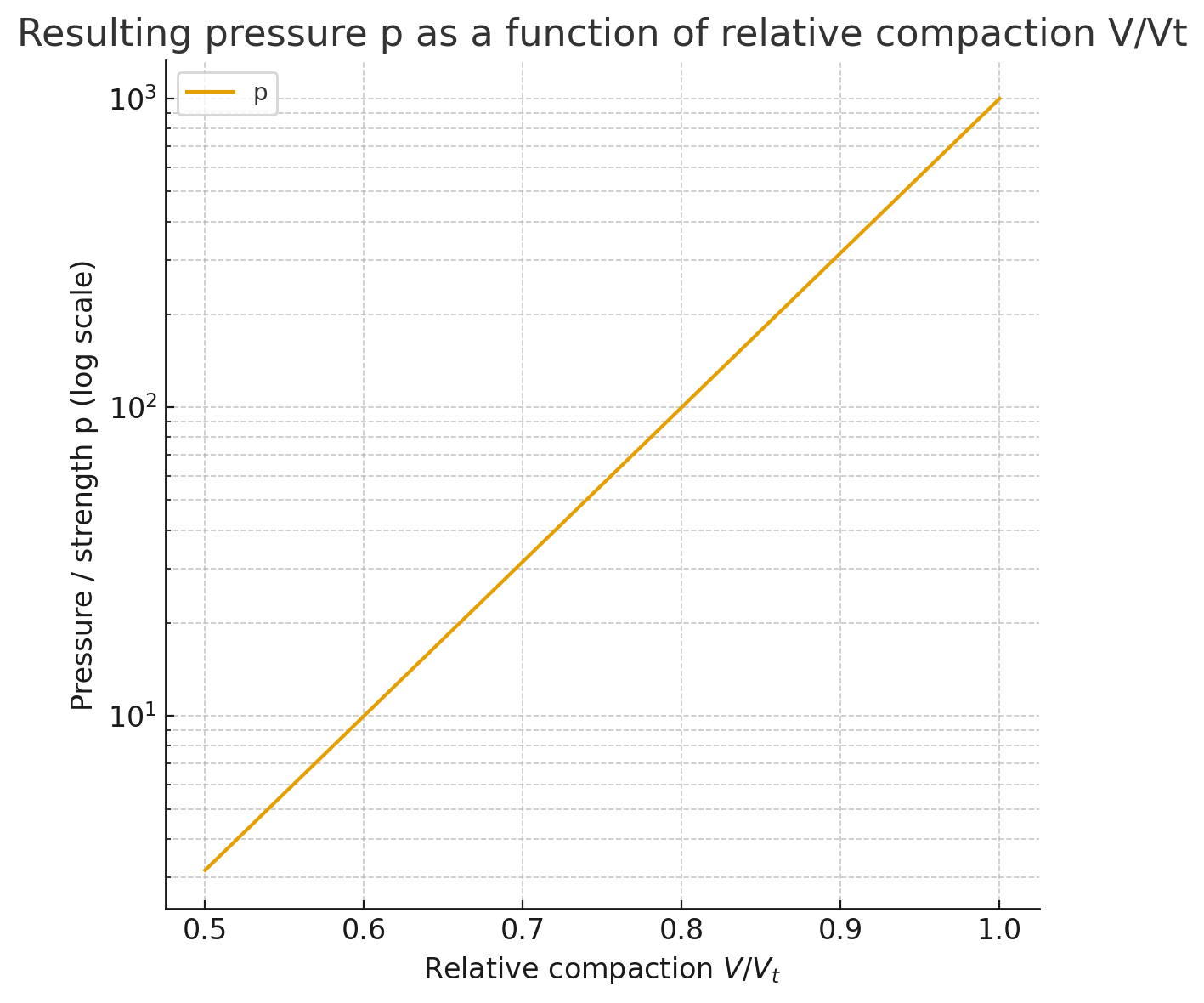
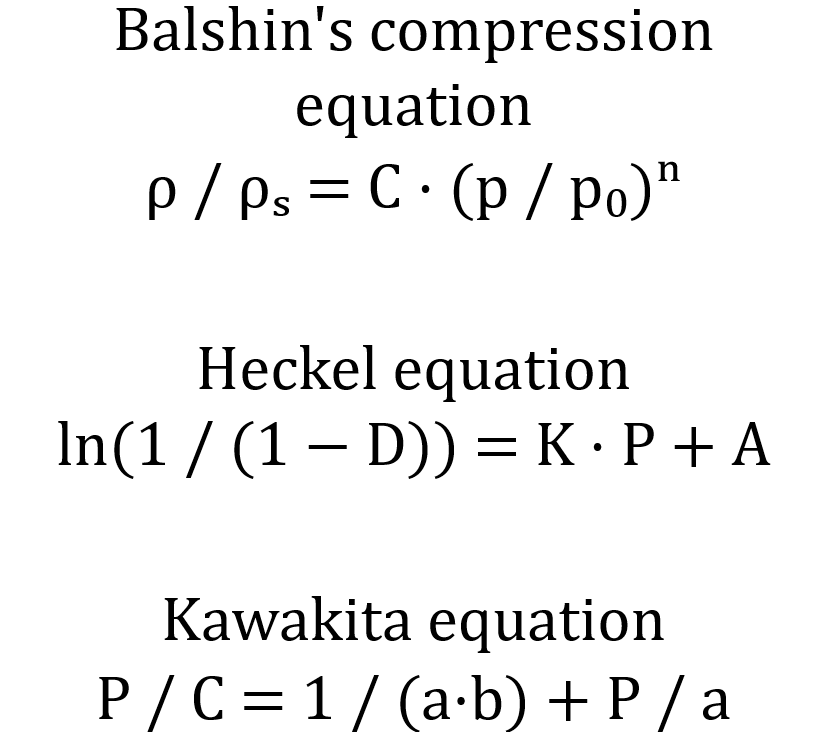
Read moreCompacting
In addition to presses, roller compactors, briquetting machines, extrusion presses and perforated presses, the process of build-up agglomeration also plays a role.
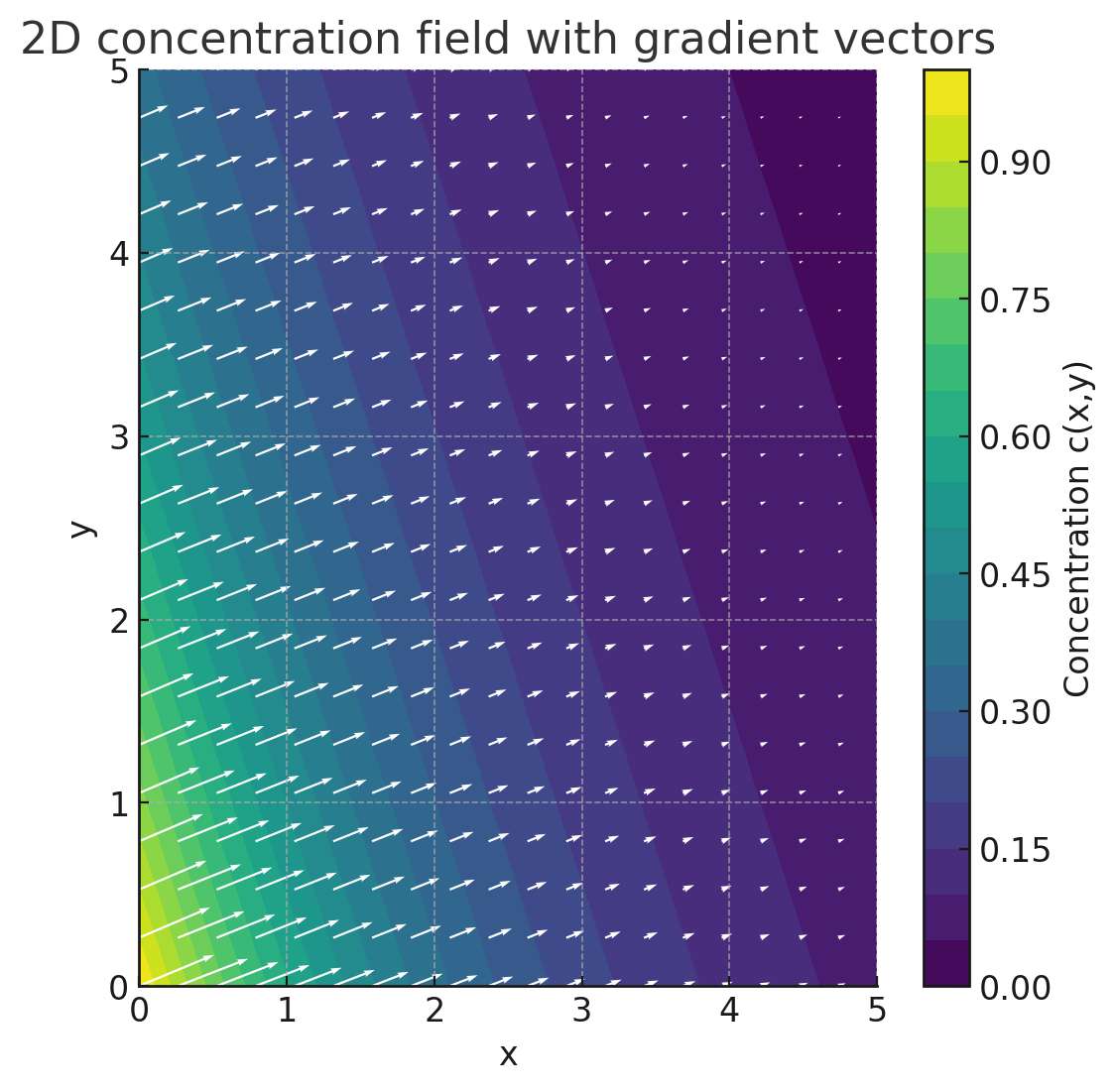
Read moreConcentration gradient
When substances move without mechanical conveying, the concentration gradient acts as a driving force.
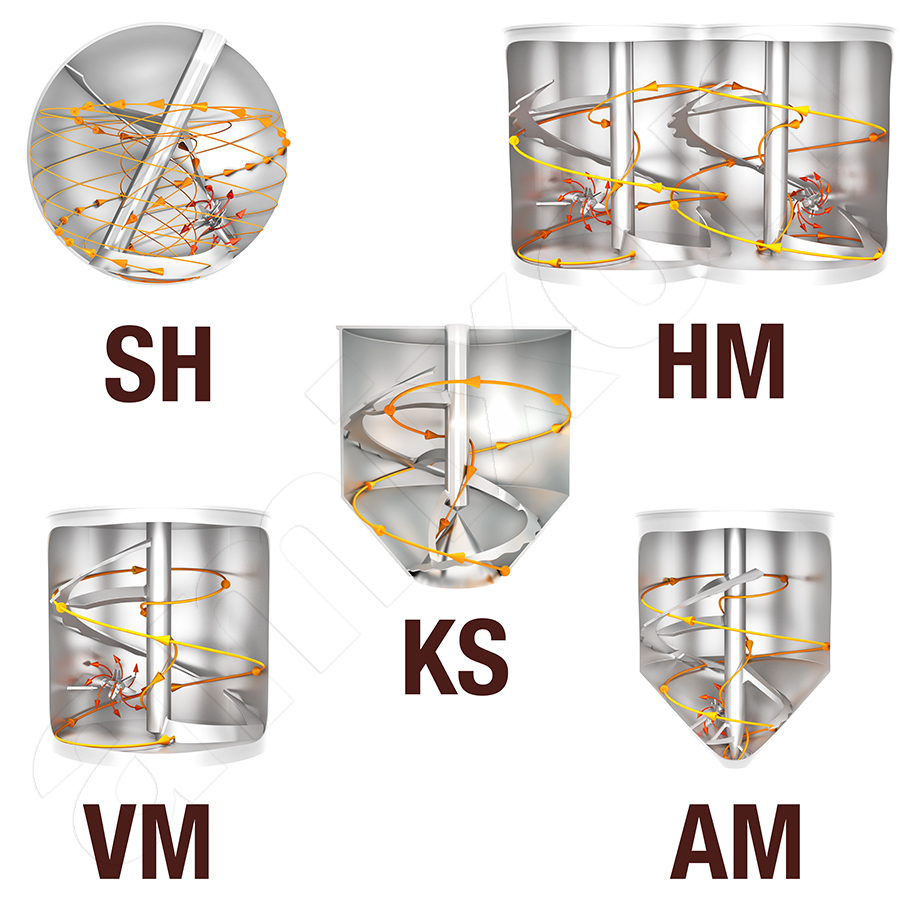
Read morecone mixer
The term "cone mixer" is used in various ways in process engineering and is not clearly defined.
Read morecontinuous mixer
A continuously operated mixer is also referred to as a continuous flow mixer.
Read moreContinuous mixer, flow through mixer, online mixer
Flow mixer, continuous mixer, continual mixer for bulk materials:
a) The mixing process takes place in static mixers in which the individual components flow into each other in free fall.
b) Dynamically moving mixing tools mix and convey the components continuously.
Read moreCross-contamination
amixon® has developed special mixing tools that significantly improve the degree of emptying and ease of cleaning.
Read moreCryogenic cooling
Liquid nitrogen has a temperature of −196 °C and can cool other substances very efficiently. The phase transition from liquid to gas increased the cooling capacity.
Read moreCrystallisation / chemical precipitation
Crystallisation is used for the purification, concentration and recovery of valuable substances in chemical synthesis and rectification.
Read moreDamp cloth cleaning
KoneSlid® powder mixers can be cleaned very easily with a damp cloth. They discharge completely and have numerous inspection doors.
Read moreDead space
An area within a process engineering apparatus that is not reached during a process step.
Read moreDeagglomeration
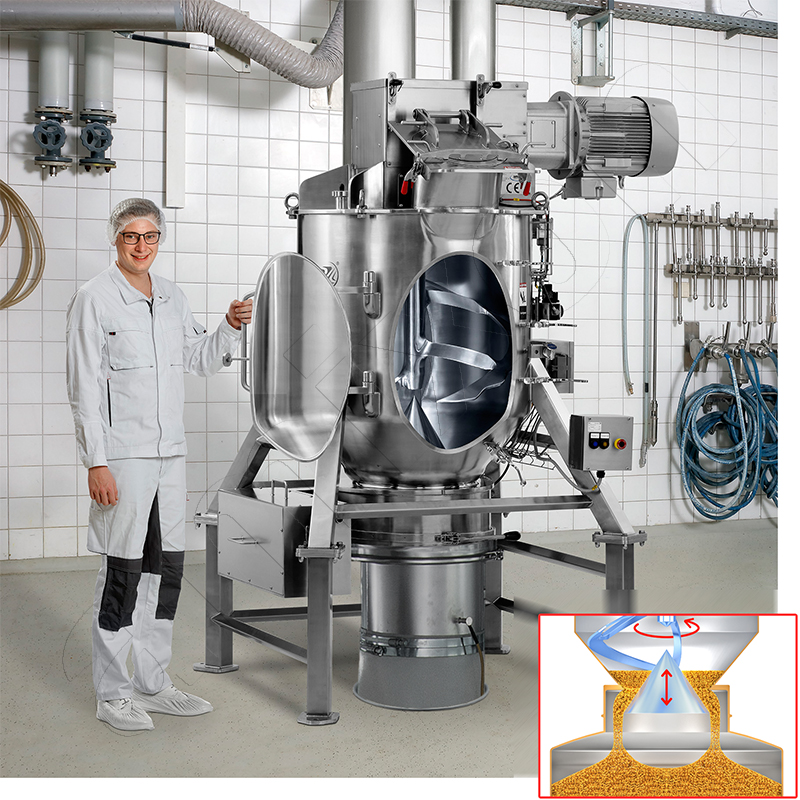
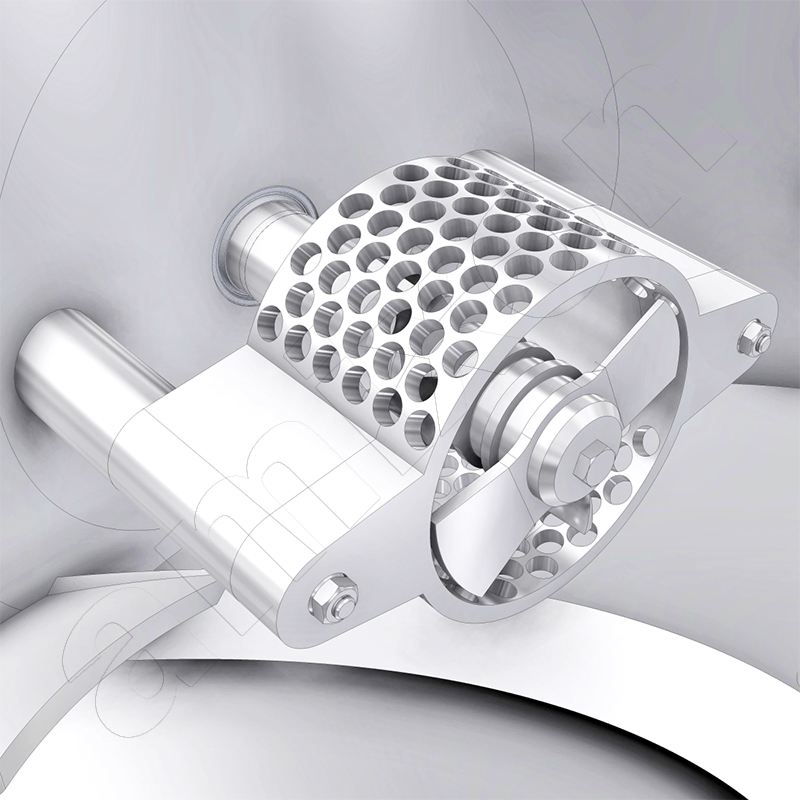
During deagglomeration, particle clusters are separated so that their primary particles are isolated. This can be done both in mixers and in crushing machines.
Read moreDiffusion coefficient
Diffusion coefficient The diffusion coefficient quantitatively describes the speed at which molecules, atoms or ions are transported in a medium by diffusion.
Read moreDiffusion constant
Diffusion in solids is relevant, among other things, when heterogeneous solids are dispersed and sintered in a nanodisperse state.
Read moreDimensionsanalysis
Dimensional analysis helps to develop calculation formulae on the basis of experiments.
Read moreDispersed agglomerate
Dispersed agglomerates are often produced during the humidification of dry, fine powders (granulation drum, fluidised bed agglomerator / eddy current mixer).
Read moreDispersing and Deagglomerating of Powder
Dispersing: Definition and importance of the process in mixing technology. A homogeneous dispersion is a bulk material in which the porosity is homogeneously distributed. If agglomerates are present, then they must be broken up until the primary particles are present.
Read moreDocking station
Docking stations for bulk material containers ensure low-dust filling and discharging.
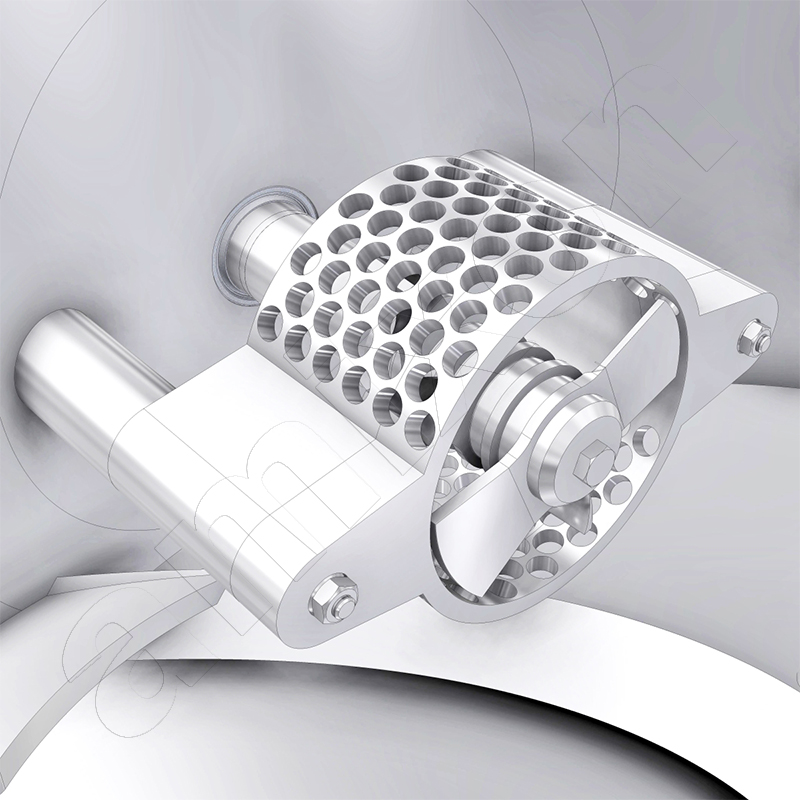
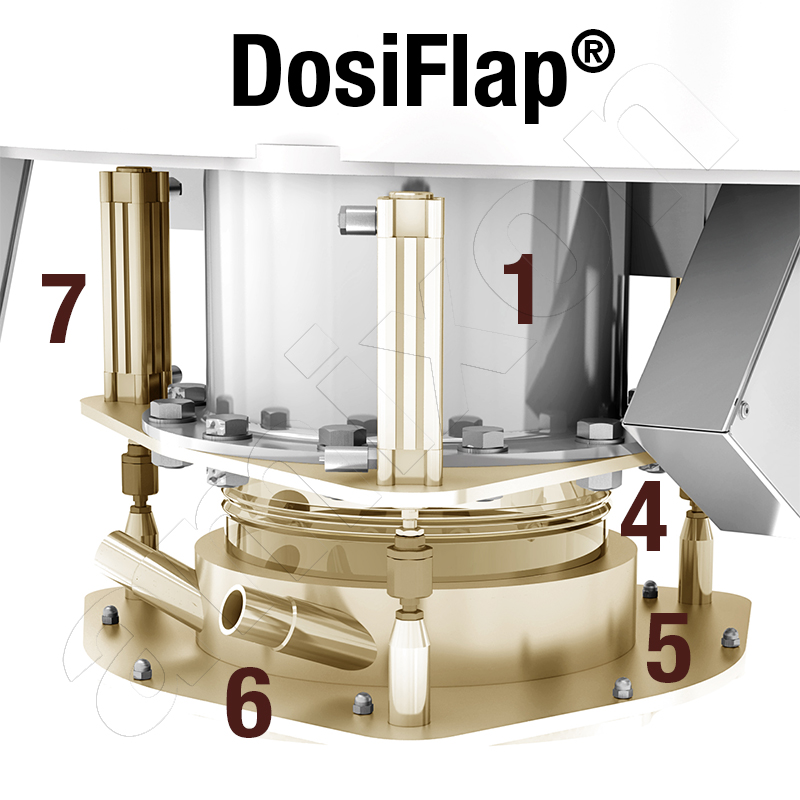
Read moreDosiFlap
DosiFlap® is a registered trademark of amixon® and refers to a dead space-free shut-off valve that is installed as a dosing and shut-off unit below powder mixers. In contrast to conventional bottom flaps, DosiFlap enables gas-tight and process-reliable shut-off of the product flow even when powder is still being discharged.
Read moreDosing accuracy
Dosing accuracy in connection with bulk solids is crucial for product quality, process stability and traceability, both in batch processes and in continuously operating systems.
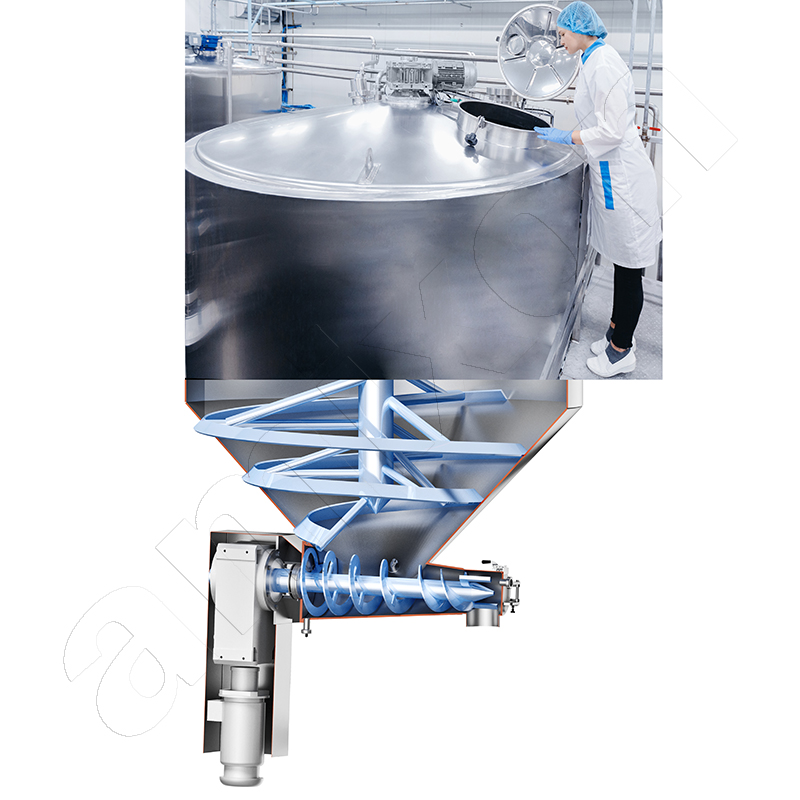
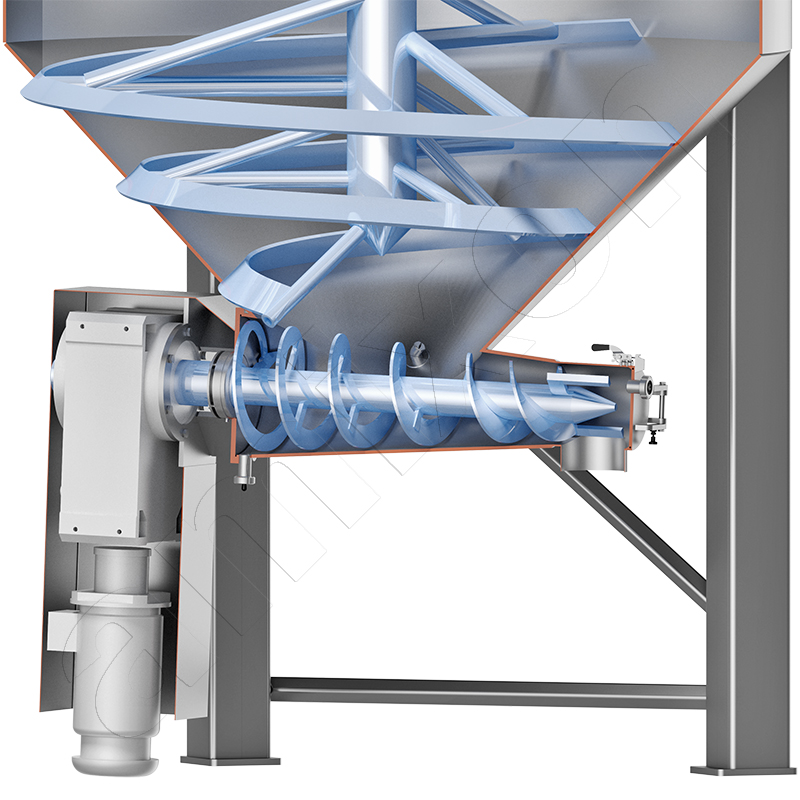
Read moreDosing screw
A dosing screw is a mechanical conveying device for the controlled discharge of bulk materials. It is used when a defined quantity of a powder, granulate or fine-grained material needs to be dosed precisely in terms of time and quantity - e.g. in mixing, filling or reaction processes.
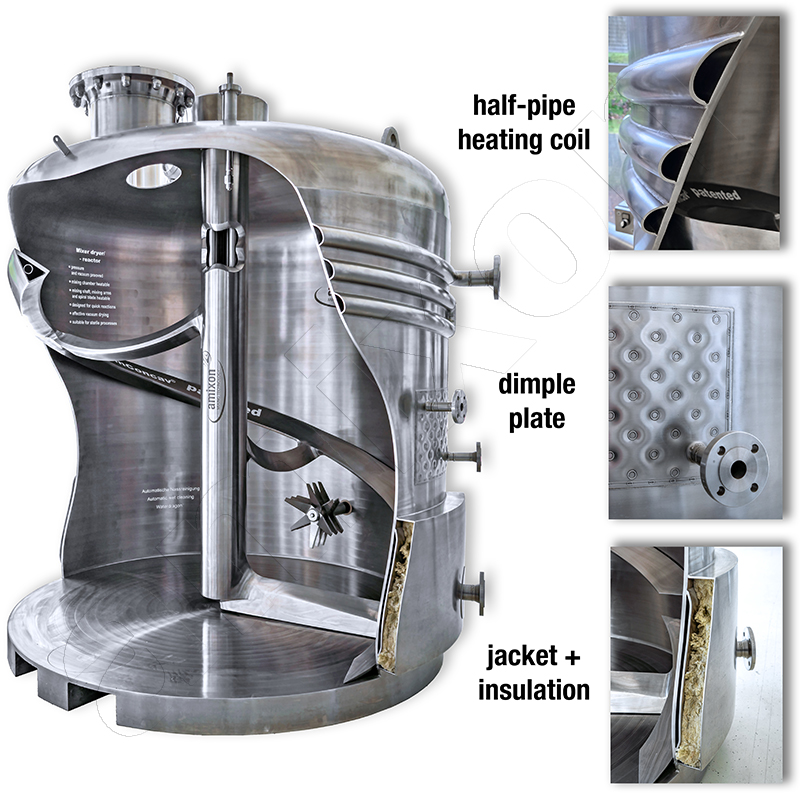
Read moreDouble jacket
Double-jacket designs can be varied, e.g.: welded outer jackets in shell form, welded half-pipe coils, structured heat exchanger plates (so-called dimple plates).
Read moreDrying vacuum Mixing drying
Contact drying, convection drying, reaction control, stripping, separation of fluids under pressure-, vacuum excitation and temperature control
Read moreEffect pigments
Effect pigments are specially developed particles that are used in coating systems – particularly in automotive paints, plastics and cosmetics – to create visual effects such as gloss, colour change (chroma shift) or depth. Unlike classic colour pigments, effect pigments do not primarily work through absorption, but through reflection, refraction and interference of light.
Read moreEHEDG
The European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group (EHEDG) is a non-profit foundation founded in 1989 and based in the Netherlands. It brings together food manufacturers, machine builders, research institutes and authorities with the aim of improving food safety through hygienic design and engineering. amixon GmbH is a member.
Read moreEmptying mixers
amixon® has done a lot of groundwork. On the subject of hygiene and complete emptying. Our solutions are called OmgSeal®, ComDisc®, SinConvex®, SinConcave® and KoneSlid®.
Read moreEmulsification Emulsifying Emulsion
If you pour a small amount of oil into a glass of water, it is not normally possible to mix the oil with the water. Oil is the lighter of the two liquids. After shaking, the oil bubbles rise from the water and settle as a layer of oil on top of the water.
Read moreEnd-of-line mixing
KoneSlid® mixers are classic ‘end-of-line mixers’. They can mix in batches or continuously. After the mixing process, they can be completely emptied.
Read moreEndowment
In process engineering, doping refers to the targeted addition of very small quantities of substances to a bulk material in order to specifically change or optimise its properties. This usually involves concentrations in the per mille or ppm (parts per million) range. The doping substances can be powdery, liquid or pasty.
Read moreEnthalpy jump
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic state variable that describes the energy contained in a system, including the volume work in relation to the environment.
Read moreEnzyme inactivation
Enzymes are biological catalysers. They control a large number of chemical and biochemical processes.
In some cases, enzymes must be specifically inactivated. This is done to prevent undesirable changes in raw materials or products.
Read moreErgonomic cleaning
Cleaning jobs are rarely popular in industry. They are physically demanding and often challenging. Cleaning process machines in particular can be complex. Depending on the design, system parts sometimes have to be dismantled in order to reach hard-to-access areas.
Read moreFDA and process equipment for APE
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) is the food and drug authority of the United States. It monitors and regulates the safety and quality of food, medicines, medical devices and cosmetics.
Read moreFermentation process
amixon® has been developing and manufacturing precision mixers and silo mixers for over 40 years, some of which are also used as fermenters - especially for highly viscous or semi-solid fermentation media. The batch sizes range from a few litres up to 100 m³. The mixers are hygienically manufactured, fully temperature-controlled and designed for particularly gentle, three-dimensional mixing - at minimum speed and maximum homogeneity.
Read moreFilling degree
The filling degree describes the ratio of the filled product volume to the available process space of a process engineering machine. This applies in particular to powder mixers.
Read moreFilling or discharge nozzles
A nozzle – also known as a connection nozzle, flange, pipe connection or inlet/outlet – is a permanently installed pipe connection on equipment or containers through which substances are fed in or discharged. The design, sealing and mounting options vary depending on the application, industry or standard variant.
Read moreFlat-bottom silos
Flat-bottom silos are used for solids when the flow behaviour of the bulk materials is poor, when several connections are to be fed with solids at the same time, or when there are structural height restrictions.
Read moreFlow properties
Unlike liquids, which only exert vertical pressure forces on the container wall when at rest, bulk solids also generate shear forces when at rest. This complicates their flow behaviour.
Read moreFluidisation, Fluidise, loosening powder by air injection
A powder is fluidised when all particles are surrounded by a gas. The powder particles no longer touch each other. The friction between them is eliminated. Fluidised powder behaves like a low-viscosity liquid. The smallest openings in the vessel (such as an incomplete weld seam, leaky fitting) lead to unwanted dust leakage. Fluidisation occurs more easily the smaller the particles are.
Read morefood hygiene
Large inspection doors are installed on amixon® mixers. They are free of dead space. Their construction corresponds to the OmegaSeal® design.
Read morefood stabiliser
In industrial production, food stabilisers are usually manufactured as dry powder mixtures.
Read moreFree-fall mixer
Unlike compulsory mixers, free-fall mixers do not have dynamically moving mixing tools that rotate within a mixing chamber.
Read moreGerm and enzyme reduction
To extend the shelf life of food, microorganisms and enzymes must be reduced.
Read moreGood Manufacturing Practice
GMP stands for ‘Good Manufacturing Practice’. These are binding guidelines for quality assurance in the manufacture of medicinal products, active substances, foodstuffs and medical devices. The aim is to manufacture products that are safe, effective and of consistent quality.
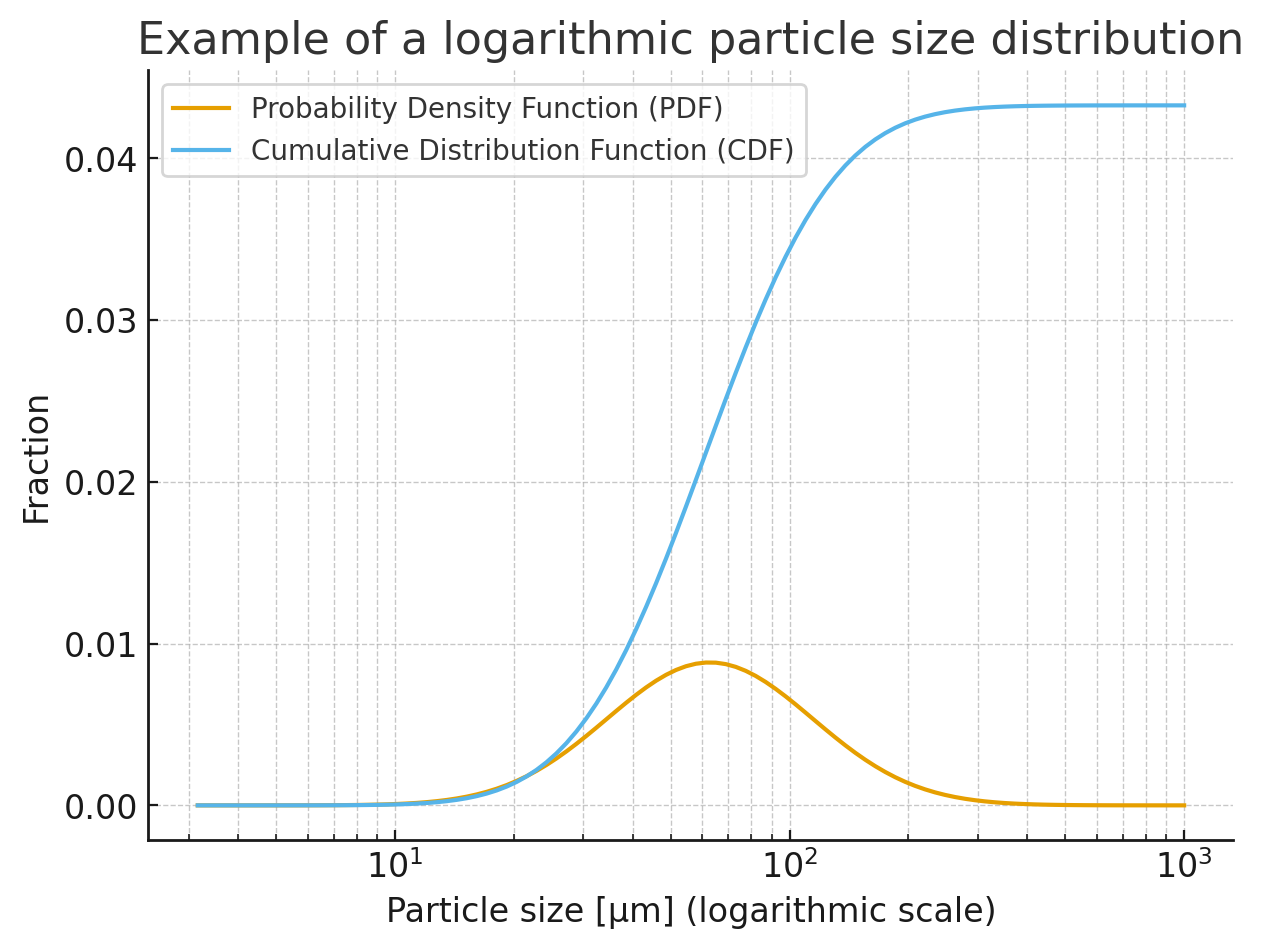
Read moregrain size distribution
For process engineers, particle size distribution forms the basis for assessing miscibility, agglomeration behaviour and product specifications.
Read moreGranulation, Granulators
The correct term is ‘agglomeration’ or ‘agglomerate granulation’. The term granulation can also describe a comminution process, e.g. when a solid is comminuted into a collection of particles / granules. Please read our detailed glossary article ‘Agglomerating’ and our blog post on ‘Agglomerating’.
Read moreGranulometry
The technical term ‘granulometry’ comes from bulk solids technology and describes the properties of dispersed substances. The focus is on the flowability and description of the particle size distribution of a bulk material
Read moreGravimetric
In process engineering, we distinguish between volumetric dosing of a powder and gravimetric dosing, for example. The latter is generally preferable. It is more complex to implement and requires suitable weighing technology. Gravimetric dosing systems are reproducible and precise. They always work accurately, regardless of the current state of the powder (loose or compacted).
Read moreGyraton Blender
amixon® manufactures the Gyraton® mixer. The Gyraton® can store large quantities of bulk material and mix it with high precision. It combines the function of a silo with that of a precision mixer. This is achieved regardless of the material properties: dry, moist, free-flowing, non-free-flowing, different bulk densities, different grain sizes, etc.
Read moreHACCP
HACCP is not a technical component, but rather a conceptual model that is translated into technical requirements. It makes a significant contribution to the manufacture of safe and hygienically sound products. Implementation is particularly challenging but essential in equipment that processes organic powders or active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Read moreHalf-pipe coils
Half-pipe coils offer similar advantages to dimple plates. In both designs, the thermal fluid can be under high pressure. The forces generated are reliably transferred to the wall of the base vessel by the numerous weld seams. This means that the sheet thickness of the half-pipe coil can be relatively thin.
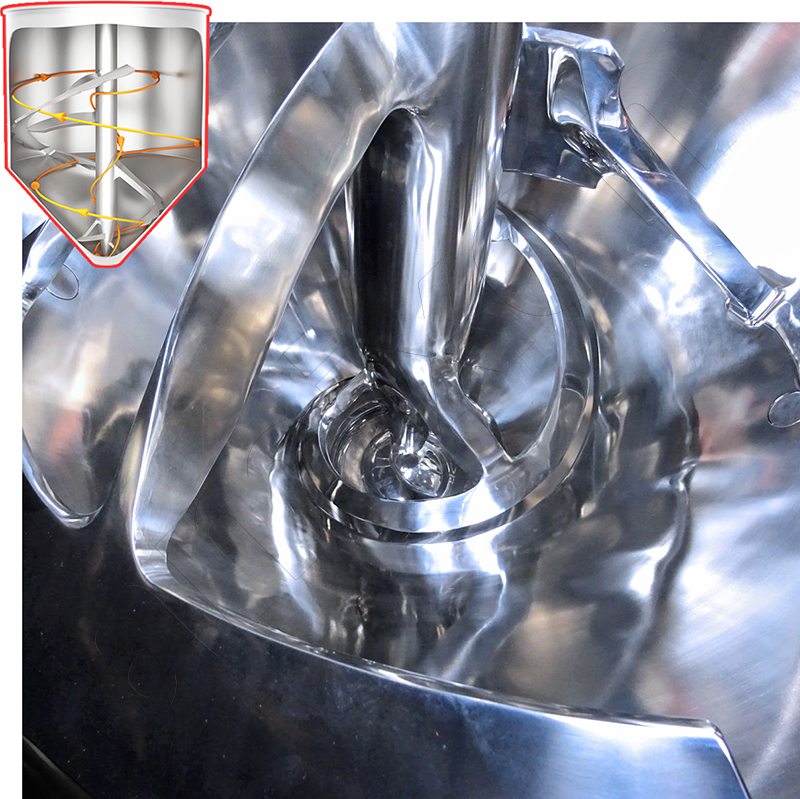
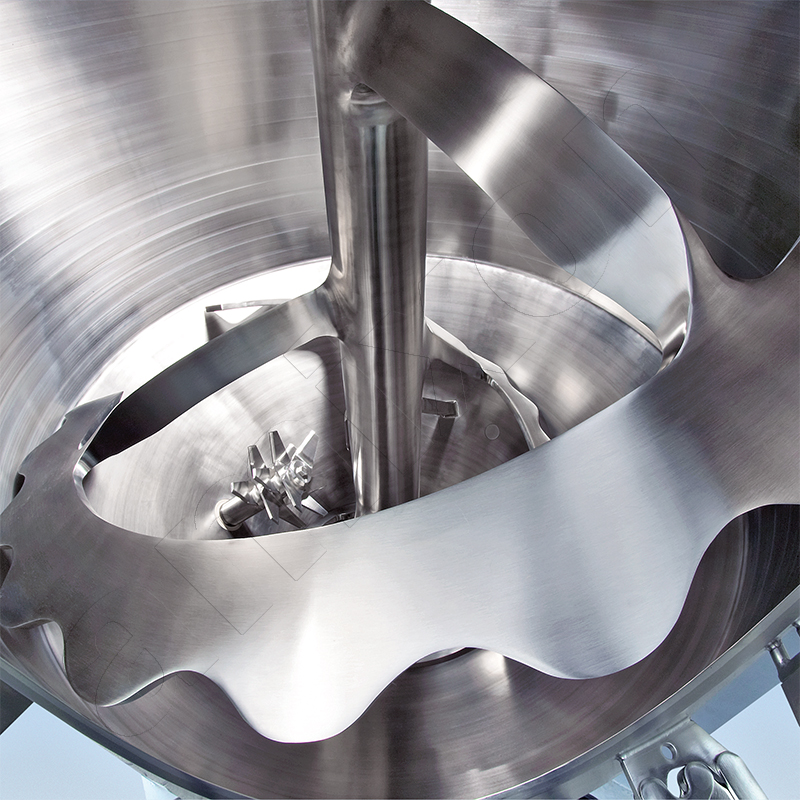
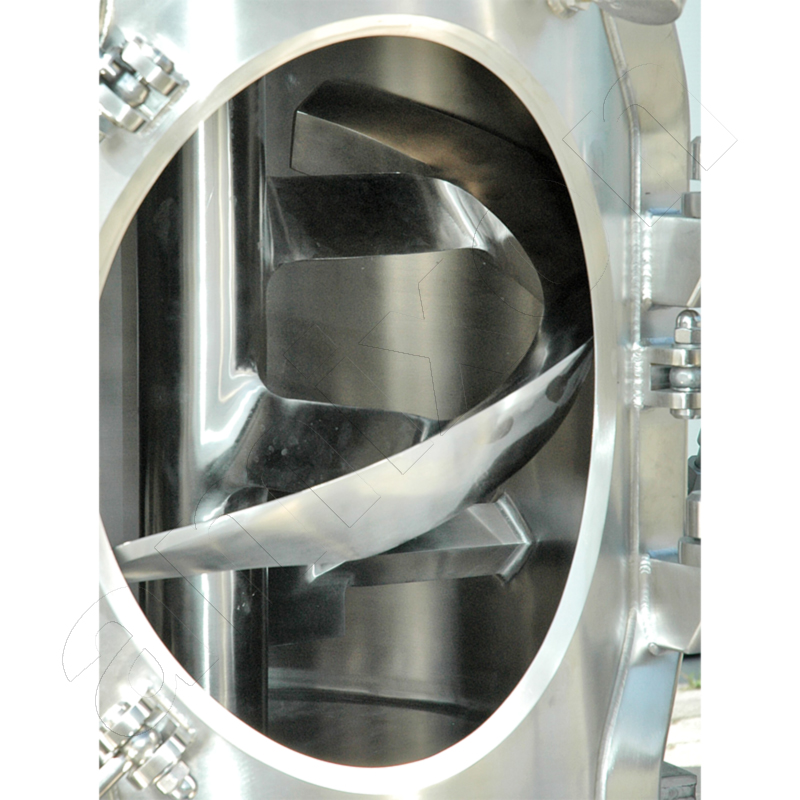
Read moreHelix mixing tools
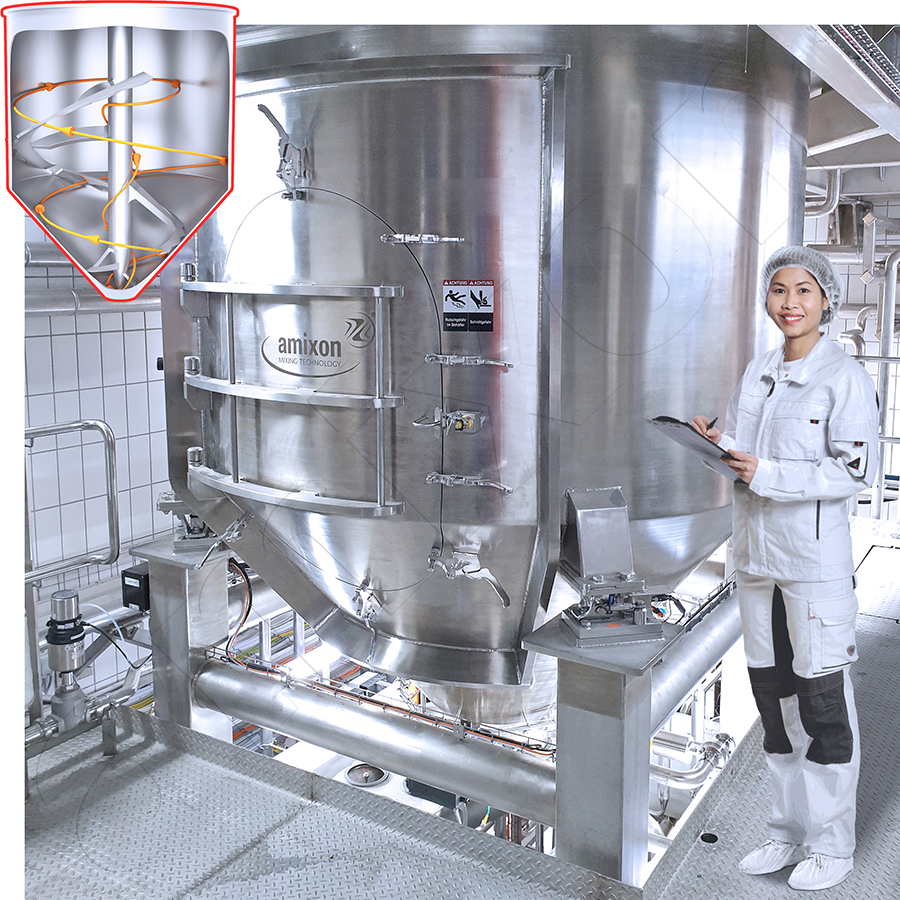
In addition to the classic helix geometry, amixon® also manufactures special mixing spiral designs known as SinConvex® and SinConcave®. These special designs improve mixing efficiency, especially for difficult-to-mix material systems, while also promoting the self-emptying effect of the mixer. They help to reduce product residues to a minimum and facilitate cleaning of the mixing chamber.
Read moreHigh-performance oxide ceramics
To improve the efficiency of ceramic processing, the reactants should be mixed homogeneously. However, this is not trivial, as the quantities of raw materials are very large. This is exactly where the Gyraton® mixer can make a valuable contribution. It mixes large batches (up to 100 m³) and guarantees ideal mixing quality. It requires only very small drive motors.
Read moreHigh-shear blades – efficient dispersion
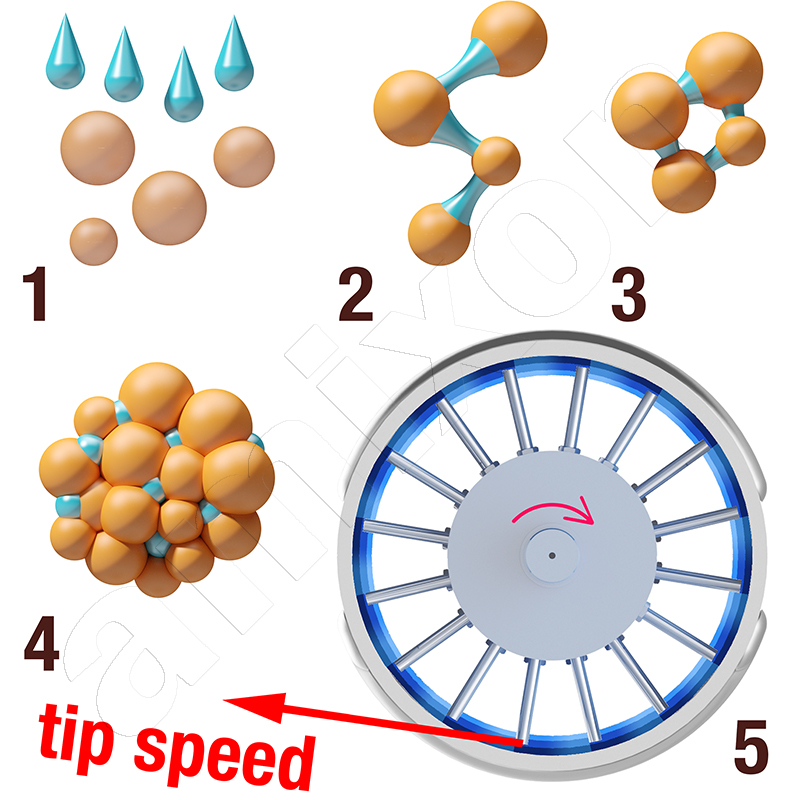
Die effektive Zerkleinerung von Mikro- und Nanoagglomeraten erfordert hohe Scherenergiedichten. Diese lassen sich durch rotierende Mischsysteme mit sehr hoher Drehfrequenz realisieren
Read moreHighly viscous
Thermal processes such as the evaporation of liquids usually result in an increase in viscosity. The same thing happens when a suspension is dried to a powder in a vacuum mixing dryer. Some materials tend to clump together, forming thick lumps. These are highly viscous and tough. amixon® synthesiser reactors/vacuum mixing dryers can handle even these kinds of materials.
Read moreHomogenization
Homogenization/ blending/ mixing of bulk materials means the uniform distribution of particle size, moisture, color and temperature of an existing mixture or bulk material.
Read moreHomogenizer
Homogenizer or mixer?
In solids process engineering, the terms "homogenizing, homogenizer" and "mixing, mixer" are used synonymously. This refers to the dispersion of one substance in another with the aim of achieving as uniform a distribution of all particles as possible. The result is a homogeneous powder mixture. Homogeneity is equated here with the ideal mixing quality of a homogeneous bulk material.
Read moreInspection doors
Inspection doors on process equipment are highly sophisticated construction elements. They must be manufactured with the utmost care. As they are safety-relevant, they must be locked to prevent incorrect operation.
Read moreInstant nutrition
The gentler the mixing process, the better a powder can be wetted. In most cases, instant powders need to be dissolved in water. amixon® mixers guarantee gentle mixing. This preserves taste, colour, appetising appearance and nutritional value.
Read moreInstant-Foods
The term "instantisation" is used in connection with the production of foodstuffs and luxury foods. However, in other contexts, such as in IT or general language usage, the term "instantisation" can have other meanings. In this case, it is based on powder technology.
Read moreInstantisation
Instantising makes powdery substances quickly wettable, dispersible and soluble on contact with a liquid.
Read moreIntensive mixing
Fein disperse Schüttgüter rieseln nicht, sie kleben aneinander. Sie neigen zur Klumpenbildung. Dies ist besonders kritisch bei sehr kleinen Partikeln.
Read moreIsoteniscope method
The isoteniscope method is a physical-chemical measuring method for determining the vapour pressure of a liquid as a function of temperature.
Read moreJoint-free
OmgaSeal® and sterile flange connections should be used where wet cleaning is carried out regularly. The smooth weld seam is by far the most hygienic seal.
Read moreKwickKlamp
KwickKlamp® is a hygienic quick-release fastening system from amixon® that can be operated safely with just one hand.
Read moreLarge fermenter: Gyraton® silo mixer becomes a fermenter/reactor
The Gyraton® mixing technology from amixon® is an innovation in the field of large-scale material processing. It uniquely combines two contrasting requirements: “absolute product protection with excellent mixing quality.” The Gyraton® mixing process meets the highest hygiene standards – even with batch sizes of up to 100 m³.
Read moreLarge-capacity mixer
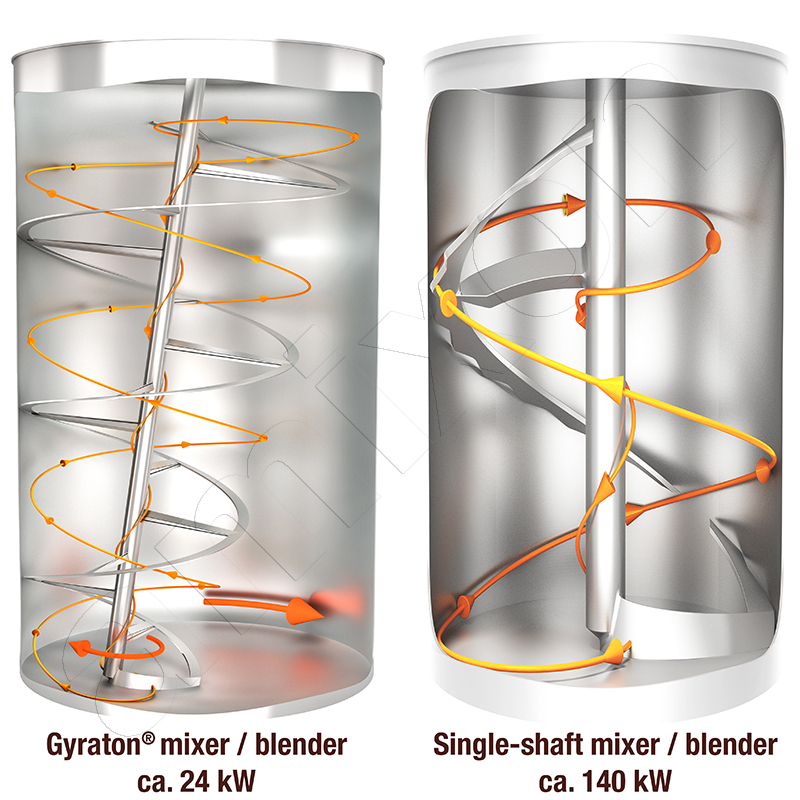
The company amixon® has developed this innovative mixing system for all types of bulk solids. It enables ideal mixing quality at very low rotation speeds of the helix mixing tool, even with batch sizes ranging from 20 to 100 m³. The technology combines high mixing quality with greatly reduced specific drive power. Compared to classic precision mixers, the drive power can be reduced by 80 to 90 percent. In return, the mixing time is extended by a factor of five to ten. That is, for example, 2 or 3 hours.
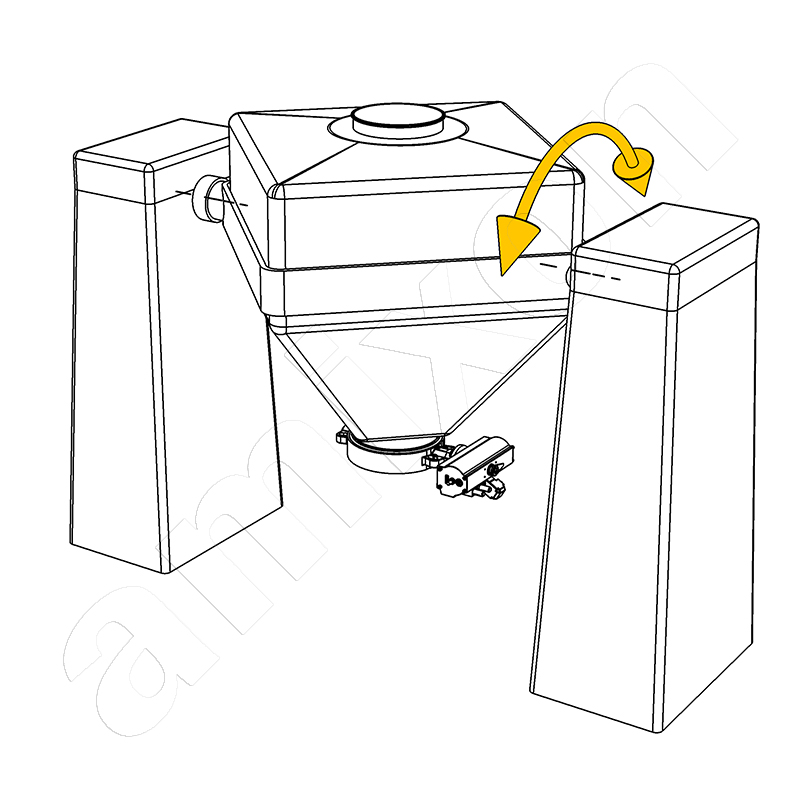
Read moreLift and lower system for mixers
Mixers that can be lowered and raised for the purpose of filling and emptying are interesting if the available space offers little height.
Read moreLiquid additives
The powder mixture must remain free-flowing despite wetting. Free from agglomerates. This makes it easy to dose and fill and ensures long-term storage stability.
Read morelithium derivatives
The most important lithium derivatives include lithium carbonate, lithium hydroxide, lithium oxide, lithium chloride and lithium fluoride.
Read moremacro trends
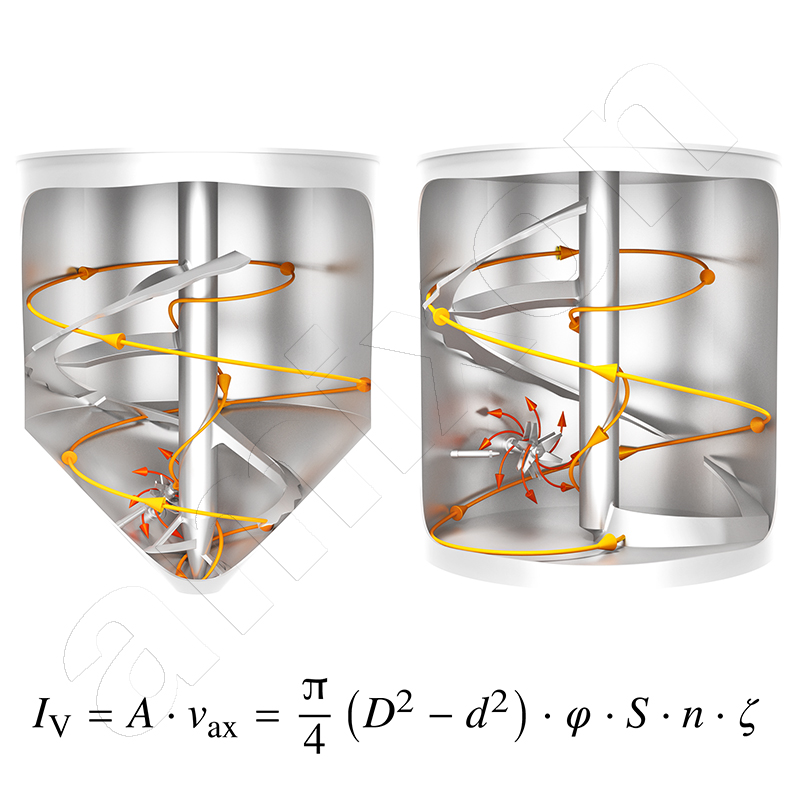
Dispersive mixing effects in a powder mixer are usually caused by the interaction of macro and micro flows.
Read moreMechanical alloying
When the possibilities of metal smelting reach their limits, powder metallurgy offers suitable alternatives.
Read moremetal soaps
Metal soaps are salts of higher fatty acids with metals such as calcium, magnesium, zinc or aluminium.
Read moremethyl cellulose
Methyl cellulose is produced by reacting alkaline-activated cellulose with methyl chloride.
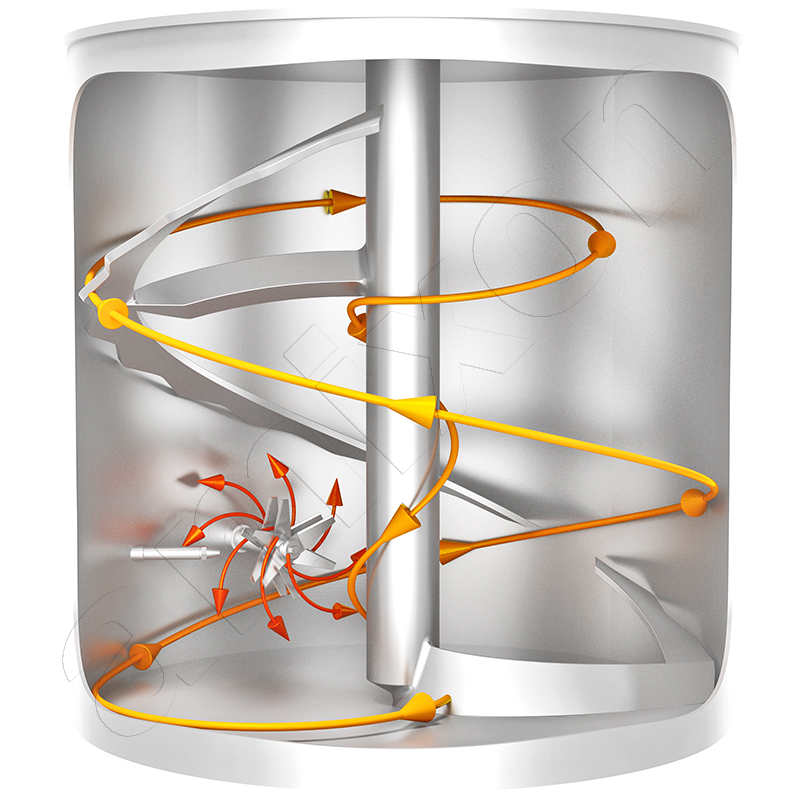
Read moremicrocondensation
Microcondensation can be used specifically in an amixon® mixer to minimally wet bulk solids.
Read moremicrotrace element
Microtracers are usually available as dry micro- or nanoparticles with a narrow particle size distribution. Due to the low concentrations used, they do not affect the product properties of the bulk material.
Read moremineral mixtures
Mineral mixtures are concentrated premixes of trace elements and finely ground minerals. They are added in small quantities to food, beverages, baby food, dietetic products and food supplements. They also play an important role in animal nutrition and in numerous soft drinks.
Read moreminimum ignition energy
The minimum ignition energy is determined in pressure-resistant test apparatus. A dispersed dust-air mixture is exposed to electrical ignition pulses of varying magnitudes until it deflagrates or explodes.
Read moreMiscibility
Hydrophobic powders are difficult to mix with water because high interfacial tensions and low adhesive forces develop. Hydrophilic powders behave differently.
Read moremix drying
Ideally, the mixing chamber, mixing tool shaft and mixing tools should be fully temperature-controlled.
Read moremixed media
Mixing technology describes the science and practice of mixing substances. It is a central area of chemical engineering and process engineering.
Read moremixer weight
The mixer weight refers to the mass of an industrial mixer in its complete structural design. It includes the dead weight of the mixing vessel, the mixing tools, the drive and bearing technology, and the support structures. Operating materials such as gear oils, hydraulic media, or thermal fluids in double jackets must also be added to the mixer weight.
Read moremixing accelerator
Mixing accelerators are twofold: on the one hand, they are supplementary mechanical tools that intensify the mixing process. On the other hand, they are chemical or physical additives that improve the miscibility of components.
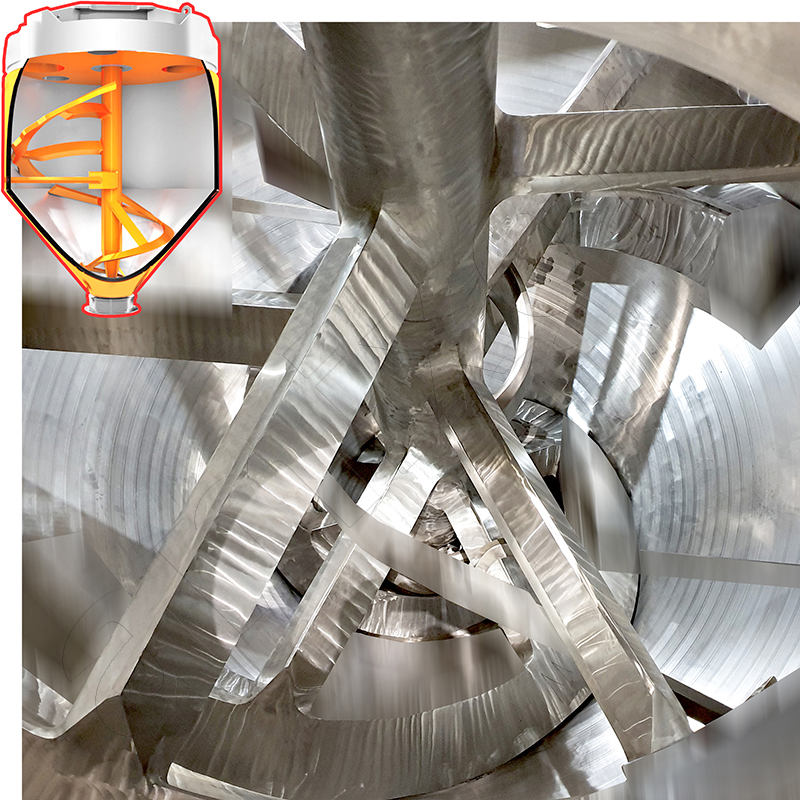
Read moremixing arm
The mixing arm is a central structural element of the powder mixer. It is firmly connected to the mixing shaft. This connection can be bolted or welded. Its primary task is to support the mixing tool. This tool sweeps over the wall of the mixing chamber at a defined distance.
Read moremixing criteria
The mixing technology used must be designed in such a way that the quality characteristics of the product are maintained during the mixing process. With an appropriate mixing strategy, some properties can even be specifically improved.
Read moremixing effect
In powder mixing, the mixing effect is the ability to rearrange the powder particles so that they are distributed homogeneously in the powder mixture. A high mixing effect is achieved when all areas of the batch are regularly and completely permeated.
Read moreMixing efficiency
Mixing efficiency describes the ratio of the effectiveness of a mixing process to the time or energy required for it. It indicates how effectively a mixer or mixing process reduces existing concentration differences in the product and achieves a specified homogeneity.
Read moreMixing kettle
The term ‘mixing kettle’ is rarely used in powder mixing. Terms such as ‘mixing room’, ‘mixing vessel’ or ‘mixing container’ are more common.
Read moreMixing plants
The efficiency of a mixer and the entire plant increases when they can empty themselves completely. This increases the output, saves raw materials and reduces waste.
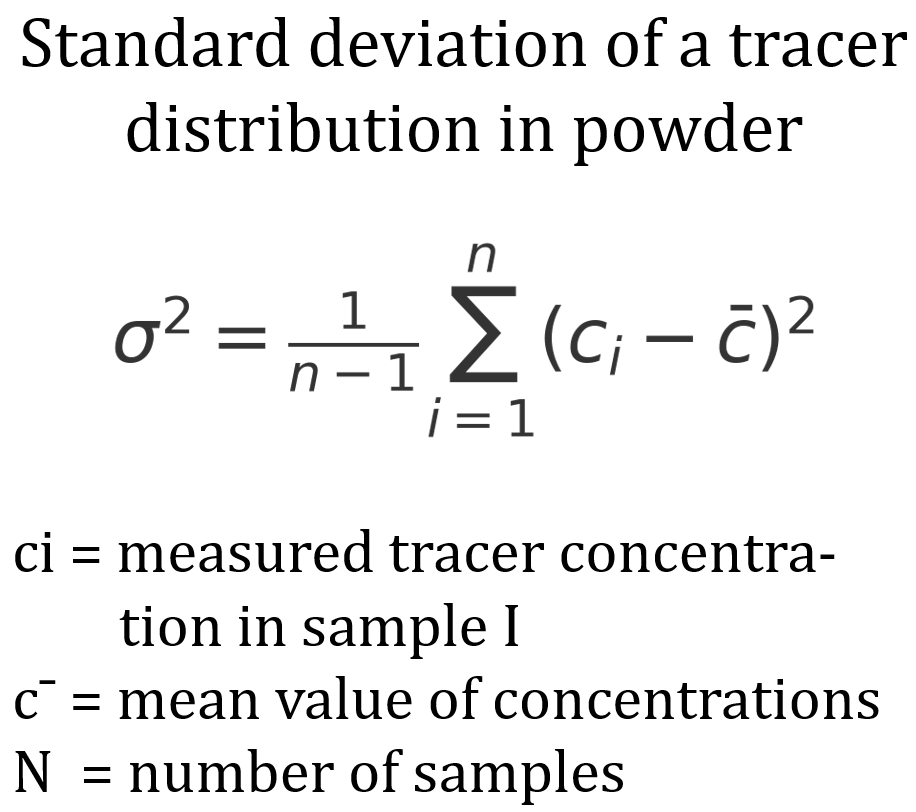
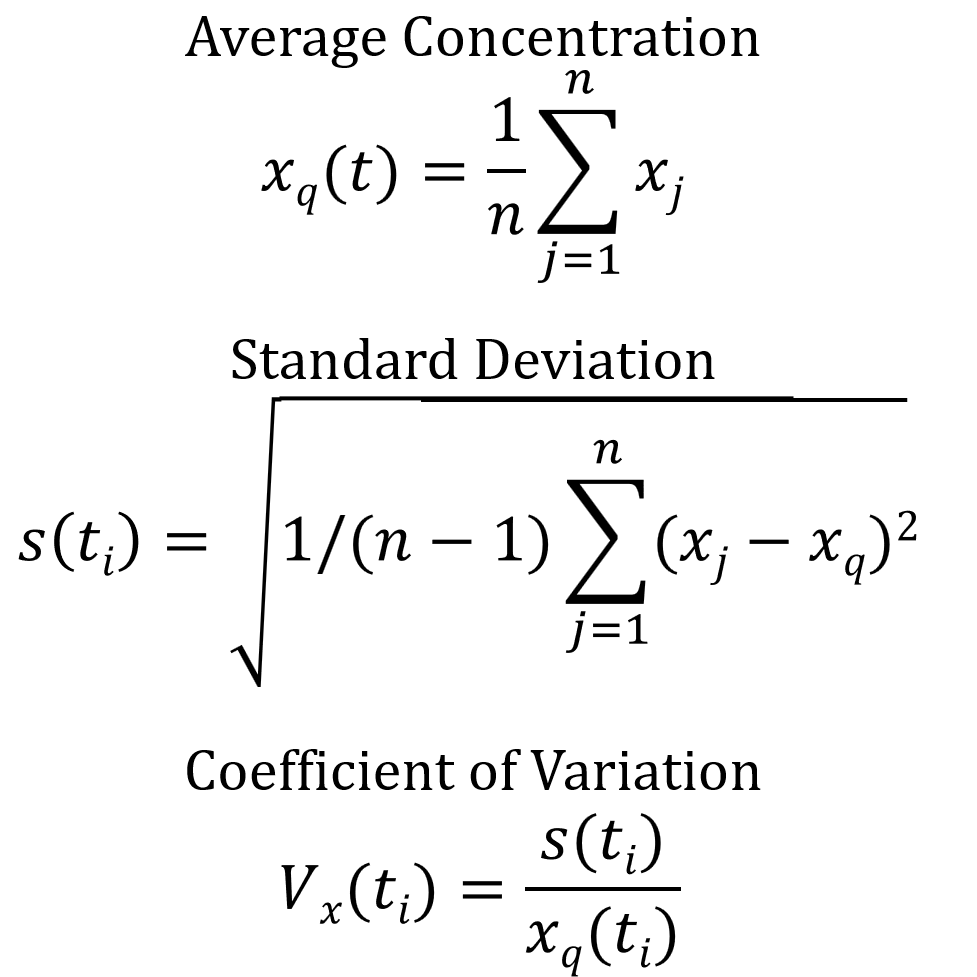
Read moreMixing quality analysis
The mixing quality describes how evenly several components are distributed in a mixture. The analysis often focuses on a minor component that serves as a tracer and is evaluated as representative of the homogeneity of the entire mixture.
Read moremixing room
The mixing chamber is the central component of every mixer. It is where all kinds of materials are mixed together homogeneously.
Read moreMixing shaft
The mixing shaft is the central, load-bearing component of an industrial powder mixer. It is motor-driven and transmits the torque as well as the bending and torsional forces to the mixing arms and mixing tools. Its mechanical design is safety-relevant and of crucial importance for the operational safety of the mixing system.
Read moreMixing solids
Liquid: In most cases, parameters such as viscosity, density and data from the shear viscometer are sufficient to describe liquids. For powders, more than 20 measurement data are required.
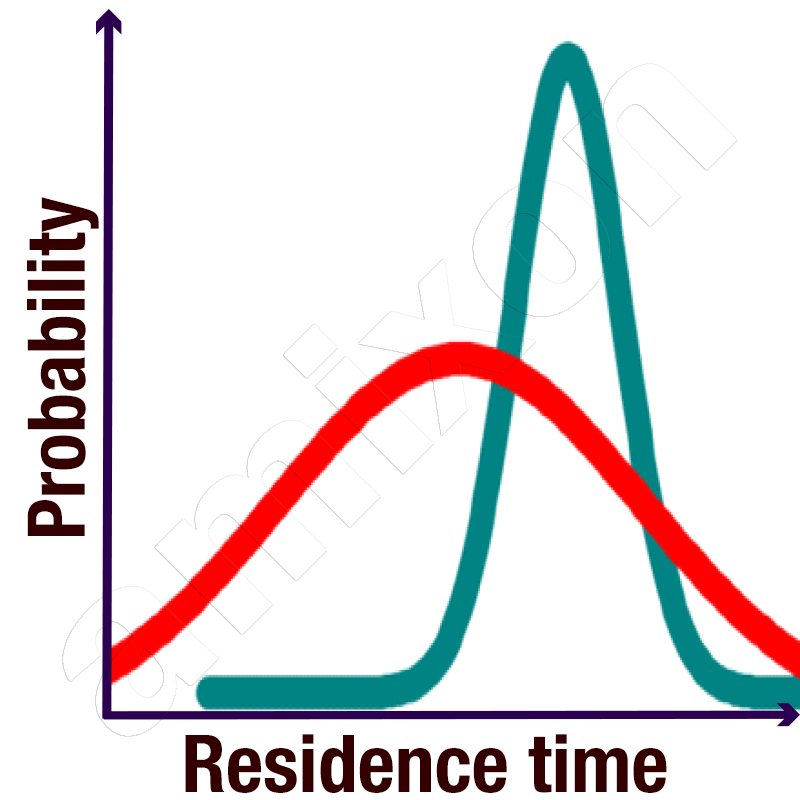
Read moremixing test
The aim is to limit the number of mixing trials. The mixing trials are usually carried out in the technical centre of the manufacturer deemed suitable. During the trial, the operating mode customary for the end user is first implemented. This is followed by a trial in accordance with the mixer manufacturer's recommendation. A further approach serves to optimise or confirm. In this way, optimisations can take place. In addition, the robustness of the process can be assessed.
Read moreMixing tools
Mixing tools are the directly acting functional elements of powder mixers. They influence the movement behavior of the mixed materials. They determine the achievable mixing intensity. Depending on their geometry and arrangement, they produce different effects. They can work by displacing, scattering, compacting, deagglomerating, or conveying.
Read moreMixing vessel
The mixing vessel holds the material to be mixed. It is usually shaped in such a way that the rotating mixing tool can mix the entire volume thoroughly.
Read moreMixture phases
Mixture phases refer to the successive stages of a mixing process. Different physical and rheological product properties dominate during these stages.
Read moreMoisture content
The moisture content describes the proportion of liquid components in or on the solid particles of a powder.
Read moremulti-step mixing method
The multi-step mixing method describes a multi-stage process for producing high-quality powder mixtures with defined liquid additions. First, selected powdered components are charged into the mixer. The mixing tool then produces a homogeneous powder mixture. Next, a liquid is added. This is done slowly and in small doses while the mixing tool is running so that the liquid is distributed evenly and no localised over-moistening occurs.
Read moreParticle size distribution
The particle size distribution describes the size and number of particles. A dispersed solid system, a suspension or an emulsion can be considered. Sometimes it is also referred to as a grain size distribution. What is meant is the same thing, namely the particle size distribution.
Read morePelletising
Many compound feedstuffs are pressed into pellets. But also wood chips for furnaces and aggregates for steel smelting. Roller compactors press the bulk material through moulds. The bulk material produced in this way is dust-free, segregation-free and free-flowing.
Read morePowder Drying
Powder drying removes liquid components from a bulk material. Liquids can adhere very firmly, especially if the powder particles have small pores. These are called capillaries. Capillary-bound liquid is evaporated by thermokinetics.
Read morepowder moistening
Powder moistening plays an important role in the process engineering treatment of bulk materials. The mechanisms of wetting are described in the glossary on the amixon website under "Wetting".
Read moreQualifying
Consumer rights are generally monitored at national level. This is to ensure that only products that do not pose a risk are placed on the market.
Read moreRotary mixer
A rotary mixer is a cylindrical, rotating device for loosening and mixing bulk materials.
Read moreRotational frequency
The terms mixing tool rotation frequency and mixing tool rotation describe the rotational movement of mixing tools. They do not only apply to mixers. The same kinematic relationships also apply to shredders, centrifuges, fans, centrifugal pumps, cutting rotors, cutter heads and rotor-stator systems.
Read moreRoughness parameter
In powder mixers, agglomerators, vacuum mixer dryers and synthesis reactors, the surface quality of the parts in contact with the product plays an important role.
Read moreSegregation Demixing
A precision blender can mix bulk materials perfectly and precisely. When they leave the blender, the powders are evenly distributed. This state must be maintained.
Read moreSeparation by Gravity
In the context of bulk solids, segregation means separation by gravity.
Read moreSilo-type mixer
The silo-type mixer primarily performs the task of mixing and is typically designed to fit visually and functionally into a silo concept. It differs significantly from the classic mixing silo, where storage is the primary focus.
Read moreSize; Apparatus size
In mixing and powder processing technology, size refers to the process volume of a processing machine.
Read moreSlope angle
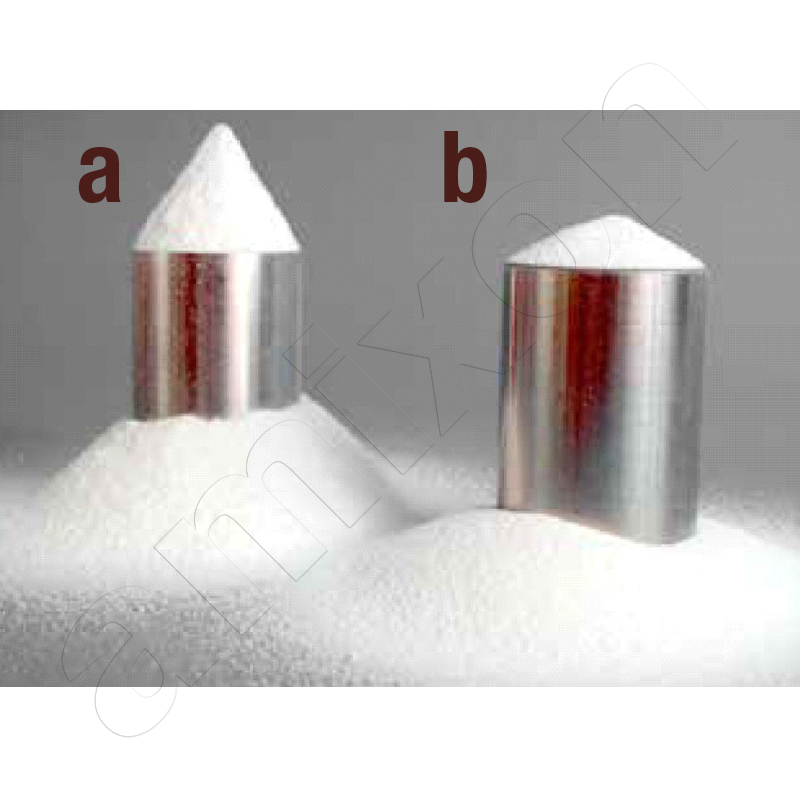
If a bulk material flows downwards from a nozzle in free fall, a powder heap is formed. If the heap forms on a horizontal plane, a more or less symmetrical cone of debris is created. This is also known as the "slope cone". From the slope inclination, initial conclusions can be drawn about the internal friction of the bulk material. The angle of repose is measured from the horizontal.
Read moreSlurry bunkers
Moisture bunkers are indispensable when it comes to the safe handling, temporary storage and demand-oriented dosing of moist, non-free-flowing products. Their design contributes significantly to process stability. amixon develops customised solutions for this purpose that are precisely tailored to the product properties and operational requirements – whether as a simple buffer container or as an integral part of a complex process step such as mixing or drying.
Read moreSolid galenics
The aim of galenics is to prepare active medical ingredients in such a way that they are safe, effective, user-friendly and stable in storage.
Read moreSolid state diffusion
Solid diffusion is used specifically, for example in powder metallurgy or engineering ceramics. Here, micro-fine metals, oxides or carbides are compacted at high pressure and then sintered. In the process, particles penetrate through the crystal lattice into neighbouring particles. This results in dense, solid composite materials with specifically adjusted properties.
Read moresolid-liquid separation
Solid-liquid separation can be carried out either mechanically or thermally.
Read moreSolids (Bulk)
There are inevitably voids between the bulk material particles, which are typically filled with ambient air. In this respect, a two-phase dispersed system is present.
Read moresolubility
Some powders can be dissolved in liquids. Gases can also be dissolved in liquids.
Read moreSteam sterilisation
Steam sterilisation of powdery goods can be conveniently carried out in the amixon® apparatus. amixon® sterile reactors also serve as vacuum mixer dryers. They are used in particular for powdered goods.
Read moreSterilisation and disinfection
Absolute (medical) sterility can be achieved on request by increasing the treatment time and system pressure. amixon® also masters these processes and can demonstrate them in its technical centre.
Read moreSuspending
Mixing of solid particles in a liquid and keeping them in suspension there, e.g. by mechanical forces. A heterogeneous mixture that tends to phase separation.
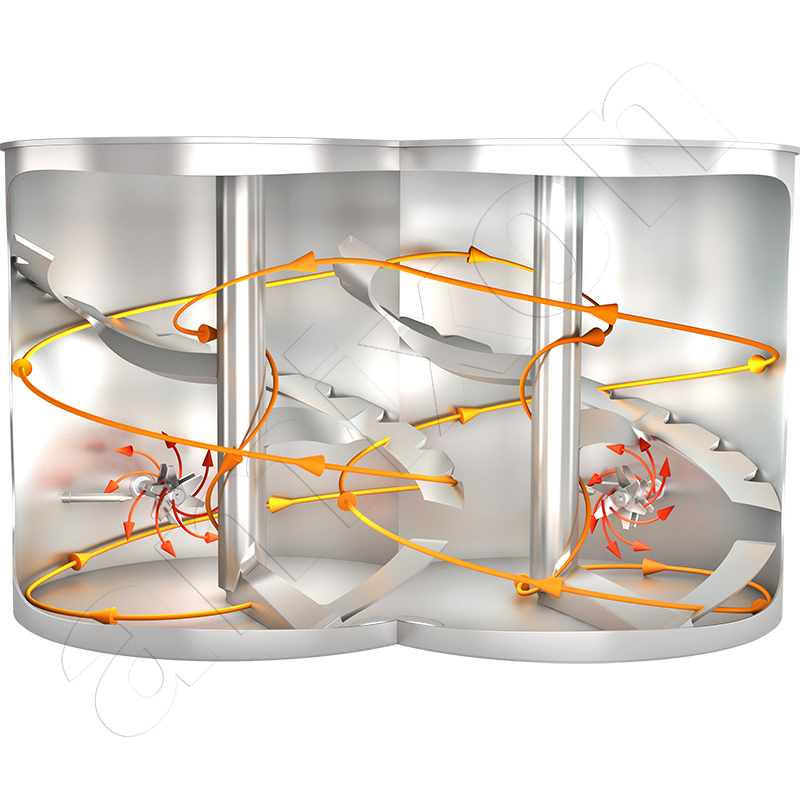
Read moreThree-dimensional total flow
amixon® defines three-dimensional total flow as the complete, dead-space-free flow of the entire mixture in the mixing chamber. The result is a statistically random distribution of the dispersed system – ideal mixing quality.
Read moretransformation of laplace
The Laplace transform is a mathematical calculation method for control systems to switch from the "time domain" to the "frequency domain".
Read moreUltrafine particles
Ultrafine particles (also known as fine dusts) are solid particles with a diameter of less than 10 micrometres (µm). In particular, nanofine particles with diameters of less than 100 nanometres (nm) are becoming increasingly important in process engineering, industry and medicine. Despite their wide range of applications, they pose a serious challenge to health, the environment and plant engineering due to their dust pollution.
Read moreUnbalance correction for rotating shafts
After completion, amixon® agglomerators undergo a balancing treatment. This eliminates both static and dynamic imbalance.
A rotating shaft with imbalance is described by an eccentric mass. This imbalance mass has a magnitude of m_u and a distance e from the axis of rotation. The imbalance product is U=m_u e.
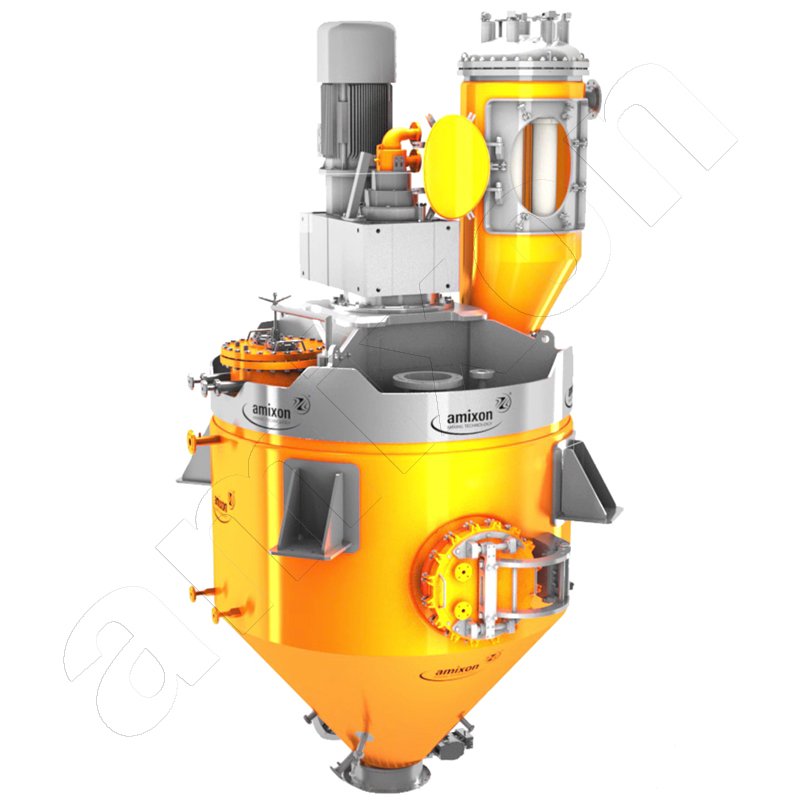
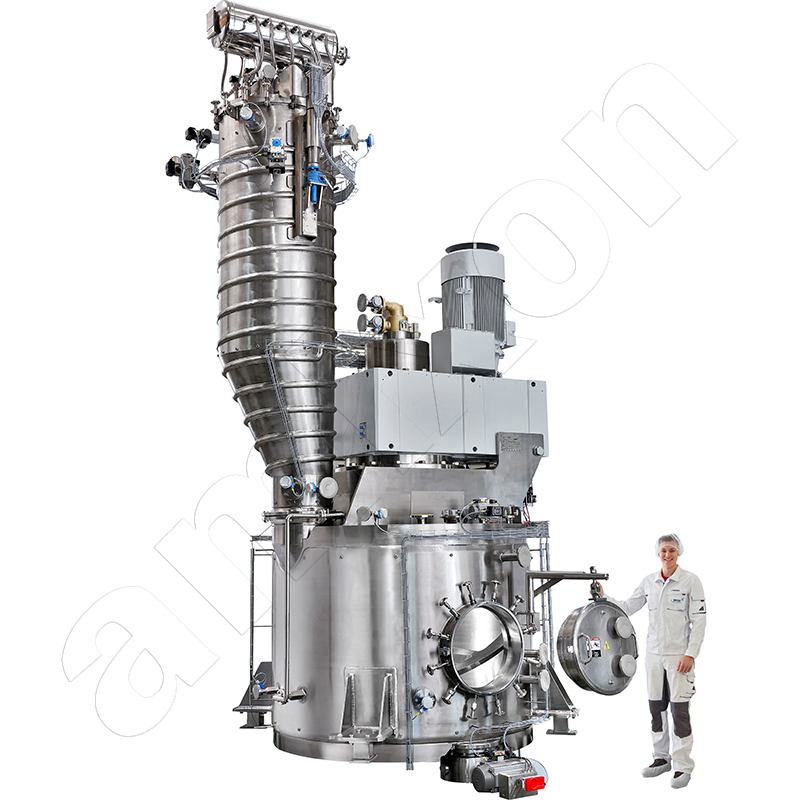
Read moreVacuum Mixer
This article on the subject of vacuum relates to mixers, vacuum mixers/dryers and synthesis reactors as used in plants in the chemical, pharmaceutical and food industries.
Read moreValidation
Validation provides documented proof that a process or system satisfies the specified requirements during practical application. To this end the devices used (e.g. mixers) have to be qualified in advance.
Read morevapor filter
Vapour filters are always required when bulk materials or powders are dried. In this case, the exhaust gas stream contains vapour as well as dust. Vapour filters have a raw gas section and a clean gas section.
Read moreweight-loss feeder
A loss-in-weight feeder measures a bulk material flow by measuring the weight loss of the storage container in real time.
Read more