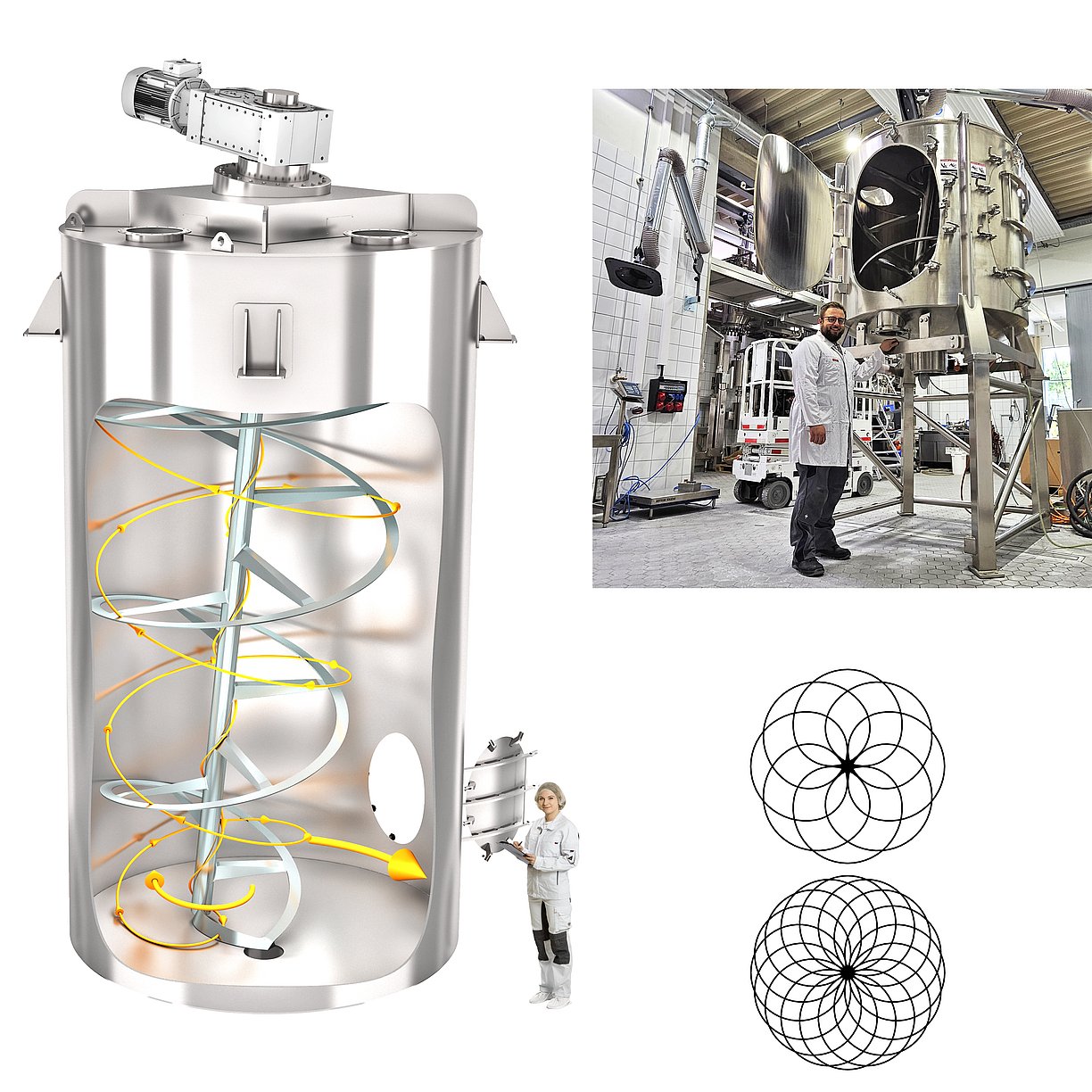
amixon® mixer/dryer for lithium salts
Lithium salts for lithium-ion batteries must be extremely pure and dry. Lithium salts include lithium oxide, lithium fluoride, lithium carbonate, lithium hydroxide and lithium chloride. Many processing steps are necessary to obtain the pure lithium salt. Almost every chemical process step ends with a drying process and blending process. Vacuum mix dryers from amixon® are ideal for the efficient and economical drying of lithium derivatives and lithium salts.
Vacuum mix dryers for lithium salts
On the basis of drying tests, amixon® can calculate very accurate projections for a wide range of drying volumes and equipment dimensions . We can also extrapolate how the drying time changes when drying takes place at higher or lower temperatures. This is also possible in cases where the mixing tool works with modified rotation frequencies.
The same applies to the calculation of the cooling time if the dry goods are to be cooled in the same vacuum mixer dryer. When calculating the cooling time, we take into account the batch size and cooling media of different temperatures.
amixon® vacuum mixer dryers are particularly suitable for drying lithium salts for the following reasons:
- The process chamber is highly clean. It is "technically tight" within the definition of TA-Luft. No particles escape, nor are foreign particles or ambient air introduced.
- Drying takes place at low speeds. The relative speeds are generally 0.8 to 1.3 m/s. This means that there is practically no abrasion and no particle destruction.
- The vacuum lowers the product temperature and accelerates evaporation.
- Extremely short drying times if a "cooling mixer" is installed under the vacuum mixer dryer. amixon® devices have a long service life despite abrupt "hot/cold changes".
- Heat transfer is extremely fast due to constant contact with the appliance surfaces.
- All appliance surfaces are heated - including the mixing shaft, the mixing arms and the spiral.
- After drying, an amixon® mixer dryer empties itself completely.
- The feeding and discharge fittings can be coupled with containment systems. This ensures a high level of product purity.
- If required, metal oxides can be added and mixed in the same mix dryer.
Vacuum drying processes can be demonstrated in the amixon® test center
A visit to amixon® is always worthwhile. You will learn a lot from talking to our experts in process engineering, design and production technology. amixon® manufactures all components itself and controls all quality-relevant breakpoints. Tests with your mixing goods will certainly lead to good results. This secures your investment decision. Calcination processes at higher temperatures can also be performed in the amixon® test center. Optionally, higher system pressures can also be used.
Gyraton® large-volume mixer / agitator / dispenser / homogenizer/ silo-blender
The more continuous and uninterrupted the typical processing steps run (suspension in digestion acids, chemical extraction by precipitation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, drying, mixing, blending, calcination, grinding), the more economical they are. Nevertheless, intermediate products must be collected in batches in order to be homogenized for the next process step. amixon® has developed a suitable mixer for large-volume homogenization. The Gyraton® mixer / blender can be operated both in batches and continuously. This innovative mixing system fulfills 5 important process requirements:
- Ideal mixing qualities are produced - regardless of the nature of the mixing goods
- The Gyraton® mixer/ blender delivers ideal mixing qualities even at a filling level of 5 %. The mixer/ blender is currently available for batches from 10 m³ to 100 m³.
- The mixer can mix abrasive goods. For this case, it can be coated with a high-performance ceramic.
- The Gyraton® blender mixes large batches with minimal energy input and maintains the particle structure.
- It meets the hygiene requirements of the pharmaceutical and food industries.
- The mixer/ blender can also be used for continuous mixing at all filling levels when placed on load cells.
Unique properties of lithium
The electric DC drive for cars has the highest efficiency of all drive systems. The quality of the battery is crucial. The battery accounts for around 40% of the manufacturing costs of an electric car. The cathode of a lithium-ion battery accounts for around 15 percent of the material costs of an electric vehicle. It consists of lithium metal oxides, which essentially consist of nickel, manganese, cobalt and other rare earth elements.
The quality of a lithium-ion battery depends on the purity of the lithium salts used. Lithium has unique properties in the group of alkali metals:
- At - 3.04 volts, lithium has the highest standard electrochemical potential.
- At 0.534 kg/dm³, lithium has the lowest specific density.
- Lithium has the highest chemical reactivity.
- Lithium has the highest melting point.
- Lithium has the highest boiling point.
- Lithium has the highest specific heat capacity .
- Lithium has the highest hydration enthalpy.
- Lithium-ion batteries have the highest specific capacity at almost 4000 Ah/kg.
Lithium extraction
Regardless of whether lithium is extracted from rock or water, it only occurs in very low concentrations in nature. The concentrations are a maximum of 0.16 %. The extraction of lithium is also possible at concentrations of 0.02 to 0.06 %. This requires that the deposit contains few and easily isolatable elements.
Lithium deposits are currently being mined in China, Australia, Latin America, Africa and the USA. Lithium can also be mined in Europe. There are interesting occurrences in Portugal, Spain, Serbia and Germany. For the reasons mentioned above, it is difficult and expensive to extract pure lithium derivatives. Each deposit has its own specific accompanying elements. This is why the treatment processes differ. The process steps are similar to the processing of other rare deposits.
Essentially, this involves classification, crushing, density separation, suspension in digestion acids, chemical extraction by precipitation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, drying, mixing, calcination, grinding, homogenization, ..... Details are kept confidential by the mining companies.
Recycling electrolytes, metal oxides and lithium from used batteries
The economic recovery of recyclable materials from used lithium-ion batteries is becoming increasingly important. The largest producers of lithium-ion batteries are China, Japan and South Korea. Recycling capacities there are growing very quickly.
The process route of raw material recycling is very similar to that of raw material extraction. They are also characterised by high energy and resource consumption. It is hoped that the partial use of pyrometallurgy will increase efficiency.
Lithium salts are used in many industries
Lithium is far too reactive to exist in nature in its pure elemental form. Pure lithium would self-ignite in the presence of atmospheric oxygen. Lithium even reacts with nitrogen to form lithium nitride. In practice, lithium salts are therefore used.
- Lithium oxide, for example, has a Li content of around 46.5%,
- Lithium fluoride has a Li content of 26.8 %.
- This is followed by lithium carbonate (18.8 %),
- Lithium hydroxide monohydrate (16.5 %) and
- Lithium chloride (16.3 %).
Lithium salts are used as fluxes in metallurgy and ceramics, as additives in the glass industry and in powder metallurgy, and as additives in lubricants. Lithium nitride is used, for example, as a carrier for the incorporation of nitrogen in alloys.
The demand for high-purity lithium salts is rising sharply
Forecasts predict a high demand for lithium derivatives for lithium-ion batteries. By far the largest quantities of lithium salts are required for the production of rechargeable batteries.
The highest purity is also required here. Lithium carbonate must not contain more than 0.4 % foreign substances.
© Copyright by amixon GmbH